Throughout history, Sweden has been responsible for a surprising number of inventions and innovations that have had a profound impact on the world. Not bad for a country of only 10 million people!
From the invention of the Celsius temperature scale in 1742 to the development of what would quickly become the world’s leading music streaming platform (Spotify) in 2006, Swedish inventions have made a lasting impression on how we all live and interact with each other over the years.
ℹ️ Keep in mind that inventions rarely come from a single person or country. In many of the examples below, Swedish inventors built on earlier ideas or worked in international teams and then made the breakthrough that turned them into practical, scalable – and often global – products. In an attempt to be as factual and balanced as possible, whenever the story is more complex or there are competing claims, I’ve tried to be clear about who did what and to mention key non-Swedish contributions as well.
Here are just a few of the most impactful Swedish inventions that have changed the world:
The Three-point Seatbelt
The three-point seatbelt is a continuation of the two-point belt, and was developed by Swedish Volvo engineer Nils Bohlin in the 1950s.
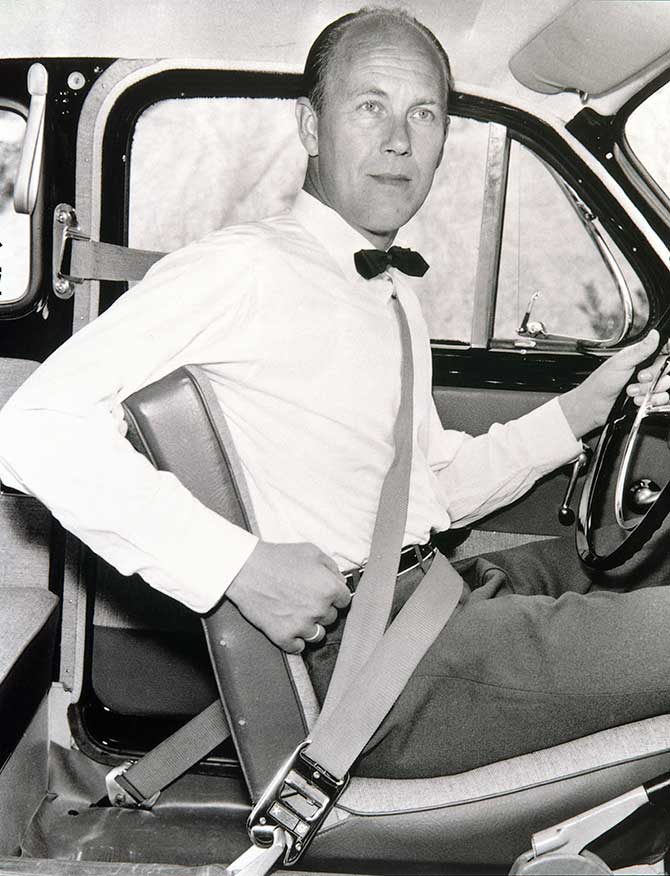

There is no denying its impact on humanity, having so far saved at least 2 million lives, with approximately 100 000 new lives saved every year (and rising).
Add to that that it saves around $5 billion in annual expenses in the US alone. Not bad!
Bohlin’s design was inspired by the seatbelts used in race cars and influenced by his work on flight ejector seats for SAAB, and it quickly became standard equipment in not only Volvo vehicles, but eventually every single car in the world.
Because in an attempt to put human lives before corporate profits, the patent of the three-point seatbelt was released in the public domain, making it a standard in almost all passenger vehicles worldwide and saving countless lives.
And with the introduction of their “multi-adaptive” safety belt in the 2026 model of the XC60, Volvo keeps improving the concept, and undoubtedly saving even more lives.
It remains to be seen if Volvo will release this latest patent to other car manufacturers as they did the original one, with a car industry that looks very different today than it did 60 years ago.
The Implantable Pacemaker
Pacemakers are small devices that help regulate the heartbeat. Early external pacemakers were developed in the 1950s by researchers such as Canadian engineer John Hopps and U.S. cardiologist Paul Zoll.

The first fully implantable pacemaker, however, was created and implanted in Sweden in 1958. Swedish engineer–physician Rune Elmqvist developed the device, and cardiac surgeon Åke Senning implanted it in patient Arne Larsson at Karolinska Hospital. Larsson went on to live to 86 and used more than 20 pacemakers during his lifetime.
Here’s a useful video explaining what exactly a pacemaker is:
Today over 3 million patients have a pacemaker, without which they could not live.
Dynamite
One of the most famous Swedish inventions of all time is no doubt dynamite, invented in 1867 by chemist, engineer, inventor, and of course the man behind the Nobel Prize, Alfred Nobel.

Dynamite is, as you probably know, an explosive material that is used in a wide variety of applications, from construction and mining, to demolition and warfare.

Dynamite was not Nobel’s only invention; he also developed smokeless powder and blasting caps. Nobel’s work with explosives led him to establish the Nobel Prize, which is awarded annually to individuals who have made significant contributions to science, literature, and peace.
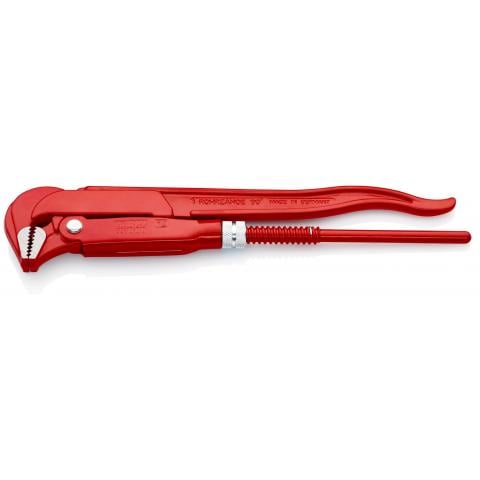
The Adjustable Wrench and the Pipe Wrench
The adjustable wrench and the pipe wrench were both invented in the late 1800s by Swedish blacksmith Johan Petter Johansson.
Though American inventor Loring Coes had already created what was called the “monkey wrench” in the 1840s, and Daniel Stillson filed the first patent for a pipe wrench, Johansson improved on both concepts with the modern adjustable spanner (with a more compact, one-handed adjustment) and a new style of adjustable pipe wrench.
Those two tools — sold worldwide under the Bahco brand — are the ones most of us still recognize today as the “adjustable wrench” and “pipe wrench”.


For those of you who are a bit confused by all these wrenches (trust me, I was too!), the adjustable wrench is a socket wrench with a movable jaw, allowing it to be used with different size nuts and bolts (making it very useful in plumbing and automotive applications where various sized fasteners are used).
If you’re in the US, I’d recommend getting a Crescent Adjustable Wrench as it’s from a company founded by a Swedish immigrant and that frankly makes damn good quality wrenches.

Crescent AT215BK 15" Adjustable Black Oxide Tapered Handle Wrench
The pipe wrench on the other hand is specifically designed to grip pipes of various sizes and can be adjusted to apply more or less pressure as needed. Here is a great example of a Swedish Pipe Wrench (though it’s made by German company Knipex).
The tools quickly became popular among plumbers and mechanics especially, who still use them to this day.
The Celsius Temperature Scale
The Celsius temperature scale is used in most parts of the world (but alas not the US…) as a way to measure temperature, and it is named after the Swedish scientist Anders Celsius, who developed it in 1742.


The Celsius scale is based on the freezing and boiling points of water, and hese two points are given the temperatures of 0 degrees and 100 degrees respectively. All other temperatures are then measured in relation to these two points.
One advantage of the Celsius temperature scale is that it can be easily converted to and from the Kelvin temperature scale, which is often used by scientists, making it a useful tool for scientific work.
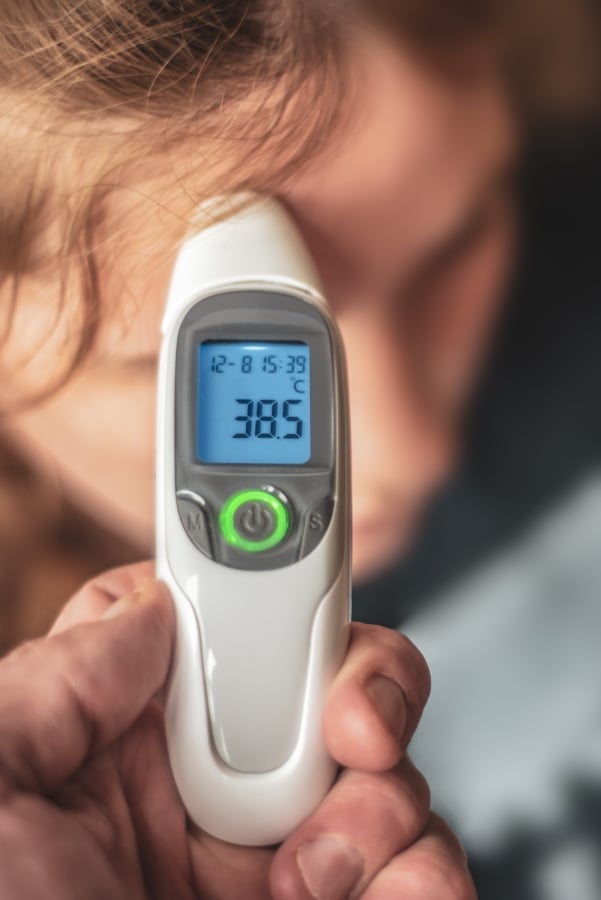
If you’d like to start practicing the Celsius scale, you can get a fever thermometer that has both Fahrenheit and Celsius, or an old-school outdoor thermometer that displays both like this classic one from Taylor.

OXO Leave-In Meat Thermometer

Taylor 481CR Dial Thermometer, 4.25", Copper

Braun Forehead Thermometer
Additionally, because the freezing and boiling points of water are well-known values, people can easily use the Celsius scale to estimate temperatures without having to use a thermometer.
The Celsius scale is also sometimes referred to as the centigrade scale.
Minecraft
In May 2009, Markus Persson (a.k.a. Notch) released a game called Minecraft, a virtual sandbox (or as I like to call it: digital Lego) where players can build anything they can imagine.

There are no rules and no goals, but players can choose to cooperate or compete with each other.

Minecraft (for Switch)
Minecraft has been incredibly popular, selling over 350 million copies as of 2025 according to Mojang’s annual 2026 report, which makes it the most-sold video game of all time. No wonder Microsoft bought the gaming franchise in 2014 for US$2.5 billion!
Due to its massive popularity, it has become much more than a game, but more a way to express oneself (as illustrated beautifully in the Vox video below).
As a result of its popularity, the game figures and buildings have become a prominent theme inside the Lego universe as well.

LEGO Minecraft The Pig House

LEGO Minecraft The First Adventure
One might call it the perfect match, as both Lego and Minecraft are block-based and have the potential to provide endless hours of creative play (without any rules or limitations).

Minecraft has also been used in education, and my mother-in-law (who teaches autistic kids) can attest to how it can be used to help children develop creativity, problem-solving skills, and spatial awareness.
The Household Refrigerator
Humans have cooled food and drinks in cellars and iceboxes for a long time, but these cooling solutions were large, bulky, and very expensive – meaning out of reach for ordinary folks.
The first household-sized, commercially viable absorption refrigerator was invented in the 1920s by Swedish engineering students Baltzar von Platen and Carl Munters at KTH in Stockholm, and it quickly became a worldwide success.
It quickly found its way into people’s homes for the first time (with Swedish company Electrolux pioneering the industry, sold in the US initially as Dometic).

Electrolux Stainless Steel Refrigerator
The Zipper
If you’ve ever used a modern zipper, you have Swedish engineers to thank (along with several earlier inventors, of course!).
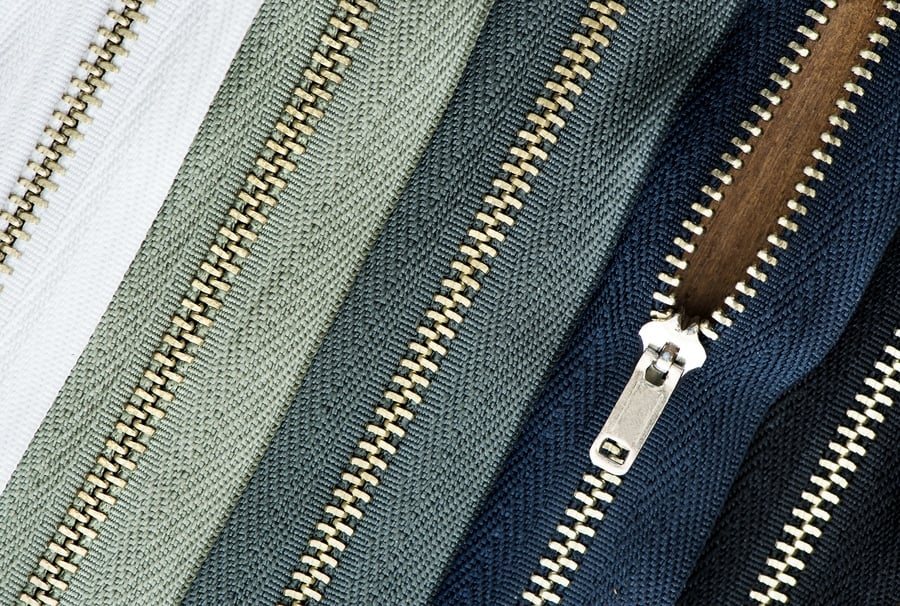

The first zipper was patented as far back as 1851 (Howe) and later 1890 (Judson), but the design was vastly improved by first Peter Aron Aronsson in 1906, and then Gideon Sundbäck in 1913 (who is usually credited as the inventor of the zipper due to his improvements in functionality and production).
Bluetooth
In the late 1980s and early 1990s, Ericsson in Lund ran a series of short-range radio projects (“MC Link” and “Penny”), initiated by CTO Nils Rydbeck. Engineers Jaap Haartsen and Sven Mattisson developed the radio link and baseband that became the core of what we now call Bluetooth.
Together with companies such as Intel, IBM and Nokia, this Swedish-led work at Ericsson grew into the global Bluetooth standard we use today.

Simply put, Bluetooth is a wireless technology that allows devices (such as smartphones, laptops, AirPods, and wireless speakers) to connect with each other easily.
The name Bluetooth comes from a 10th-century Danish king, Harald Bluetooth, who unified Denmark and Norway (and was a notoriously good communicator). The real reason behind the name is supposed to be a shared interest in Vikings among the team leads, and because all the companies involved in the development of the technology had a blue brand/logo.

Bluetooth is also an important part of the “internet of things,” which refers to the growing trend of connecting everyday high-tech objects (such as robot vacuums, smart watches, etc.) to the internet.
One advantage of Bluetooth over other wireless technologies is that it uses very little power, which helps conserve battery life in devices that use it. Bluetooth is also relatively simple to set up and use.
In addition, it’s relatively inexpensive for manufacturers to add Bluetooth capabilities to their products.
The Modern Bolt Cutter
One of the early modern bolt cutter designs that went into large-scale production was created in 1866 by Jonas Jönsson Byman in a small village in Jämtland, Sweden. It enabled people to cut bolts, chains, padlocks, and metal wires with ease, and would become an iconic tool still in use 150+ years later.
However, as Jonas tried to get his wooden prototype made in metal, the metalworker he contracted swooped in and submitted the design to the Swedish patent office without his knowledge.

So when Jonas got his first metal bolt cutter delivered and tried to apply for a patent, he got a rejection letter with the explanation that someone else had already submitted the exact same design.
This sadly resulted in his life taking a turn for the worse, ultimately resulting in him leaving his wife and 7 kids behind to emigrate to America (where he worked as a builder for 12 years).
He eventually returned to his family, built a new house and workshop, but died shortly after at 51 years old.
Both the wooden prototype and the first metal bolt cutter he had made still exist today as proof of his accomplishment, but the actual inventor never did get the rights to use and sell his brilliant invention during his lifetime.

(apologies for the sad story, but I had to give credit where credit is due!)
The Screw Propeller
Several inventors were experimenting with screw propellers in the 1830s, including Francis Pettit Smith in Britain and Swedish engineer John Ericsson.
Ericsson’s later work in the U.S. on propeller-driven warships showed how powerful the technology could be and helped make screw propellers standard in modern shipping.

Ericsson grew up in Sweden and quickly became a very promising engineer working with railroads and canals. He eventually found his way to the industrial epicentre of Europe, England, where he started honing his inventor skills working on locomotives and steam engines.
He went on to become interested in shipbuilding, which is how he invented and built the first propeller-driven ship, a design that would be used to take a ship from England to America. But his design wasn’t an instant success, and it wasn’t until he moved to America that he started to see the fruits of his labor.

In the US he continued his development of the propeller and a hot air engine he had started working on in London, and soon he was collaborating with numerous mechanical factories across the states.
His big breakthrough came when he helped to build the propeller-driven warship Princeton, that ended up winning a race against the famous British steam boat Great Western.
The propeller was a major breakthrough in maritime technology and allowed for much faster ships. Ericsson’s design was quickly adopted by navies around the world.
Today, propellers are still used on ships, although they have been replaced by more efficient designs in most applications.
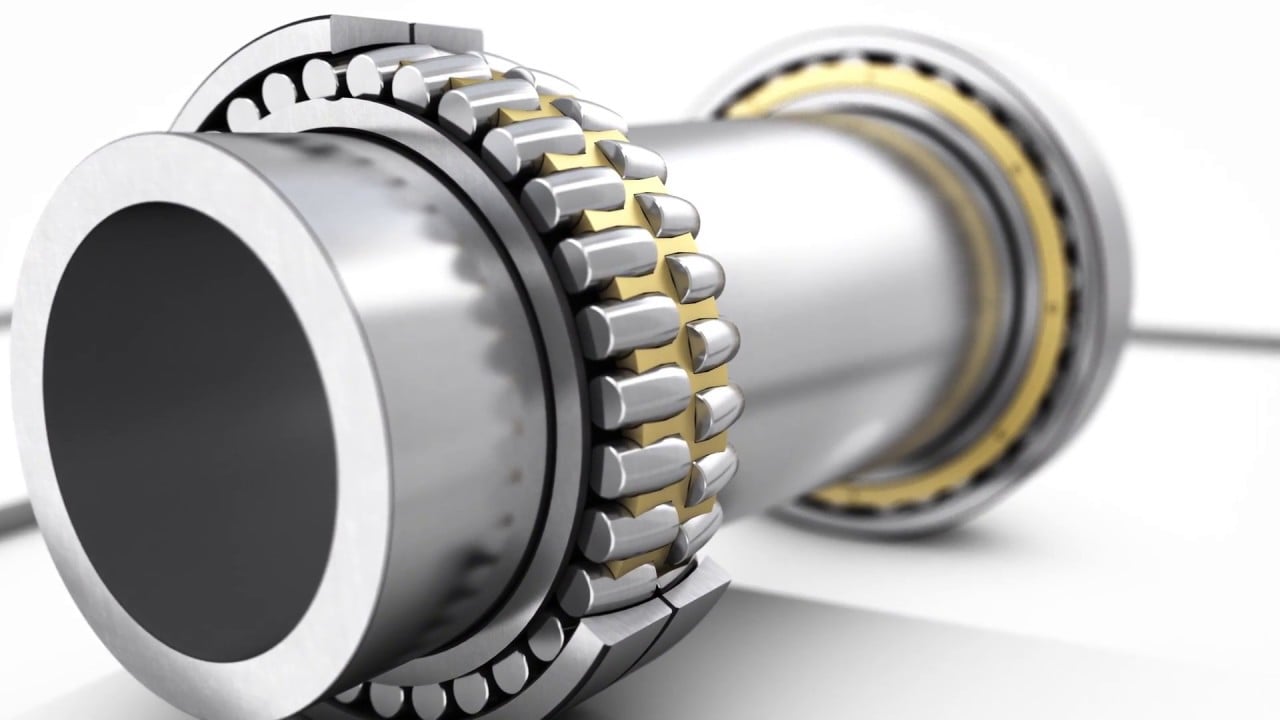
Spherical Ball Bearings
After finishing his engineering studies at a technical school in Örebro, Sweden, in 1894, Sven Wingquist worked at various factories and workshops in both Sweden and the US for the next few years.
He eventually earned a job as an engineer at Gamlestadens Fabrikers AB in Gothenburg, and was tasked with figuring out a way to prevent machines from stalling and breaking all the time.
After some analysis he pinpointed the cause to bearings that were too rigid, and of generally bad quality (bearings primarily came from Germany at the time).
He started operating an experimental workshop meant to foster improve ball bearing technology, which in 1907 turned in to the what is now the world leader in the same field; SKF.
After numerous studies on what the most efficient type of bearing would be, he settled on a design with self-aligning double-sided spherical ball bearings in 1907, which would significantly stop machines from stalling.
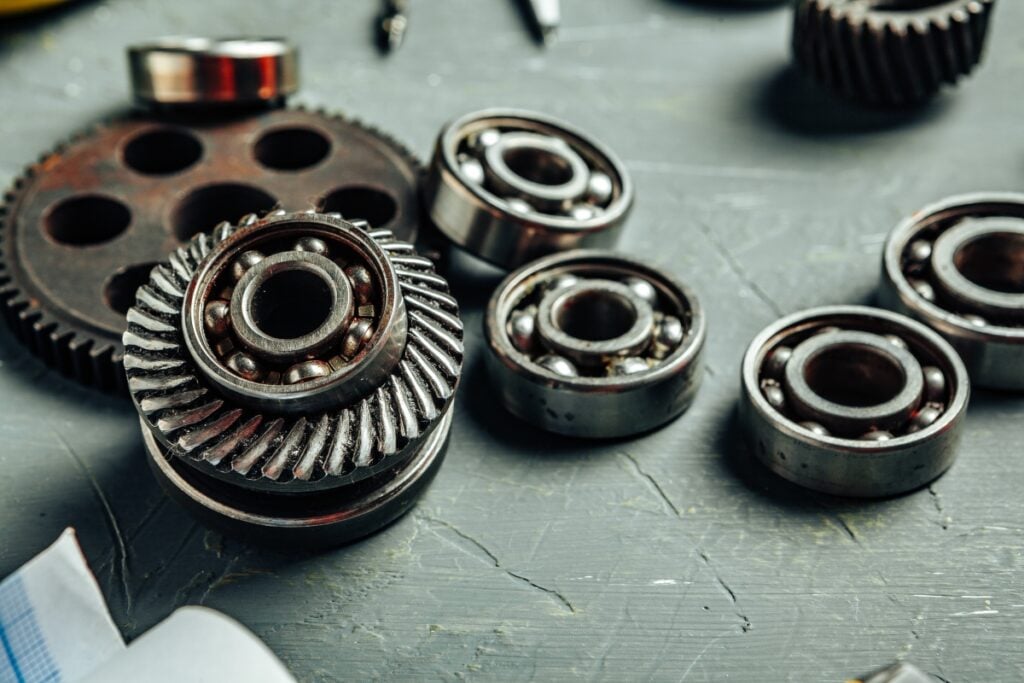

Wingquist patented the spherical ball bearing the same year, which would allow for greater flexibility and load-bearing capacity than traditional bearings.
These bearings are now used extensively in a wide range of industries, from cars and trucks, to medical equipment and construction machinery.
In fact, Sven and two young engineers at SKF were the ones who founded Swedish carmaker Volvo, which was initially meant to be a brand for one of his bearings (as Volvo means “it rolls” in latin).
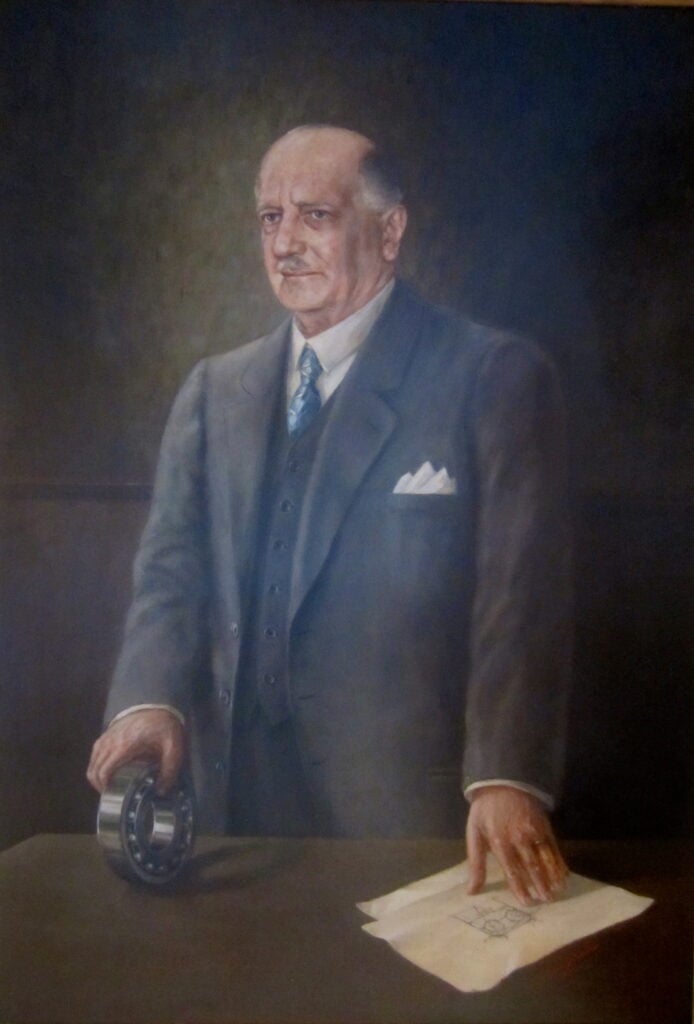

Wingquist’s other notable inventions include the roller bearing and the anti-friction ball bearing. Both of these innovations helped make SKF a world leader in bearings and other precision components.
Here’s a video from SKF explaining their bearings:
The First Color Graphics Display Card for PCs
In 1979 Håkan Lans applied for a patent for a system that could display color graphics from a computer to a monitor, and in 1981 the patent was registered in the US Patent Office.
He is thus generally credited as the inventor of the technology used to operate color displays on computers, or in simpler terms: the basis of all computer graphics cards (such as the ones modern-day giants Nvidia and AMD manufacture).

His invention has not only been hugely impactful on a global level, it has also produced plenty of intrigue and conflicts.
Many American and Japanese computer manufacturers (including Apple, IBM, Dell, Compaq, Hewlet-Packard, Hitachi, and Gateway) recognised the potential in the technology, and started using his patent in their computer systems, but without licensing the rights to do so.
Lans eventually signed licensing deals with Hitachi and IBM, which prompted most of the others to follow suit (including Apple and HP) — but Dell and Gateway would according to Lans keep using his technology without the license to do so. Lans also committed to donating any license fees he’d receive to charity.
This led to lengthy legal proceedings that hasn’t really been resolved to this day — and there are certainly questions on how unbiased the US courts actually were in their treatment of the Swedish inventor versus the US tech giants that was using his patent.
Whether or not he will get the licensing fees from Dell and Gateway is unclear, but what is clear is how impactful Lans’ invention has been on modern computer systems around the world.
The First Practical Telephone Handset
Alexander Graham Bell patented the first telephone in 1876, but Swedish company LM Ericsson was one of the first to put earpiece and mouthpiece together into a single handset that you could comfortably hold to your face.
But not even Bell was first, as we now know that it was Italian Antonio Meucci who invented the first telephone.
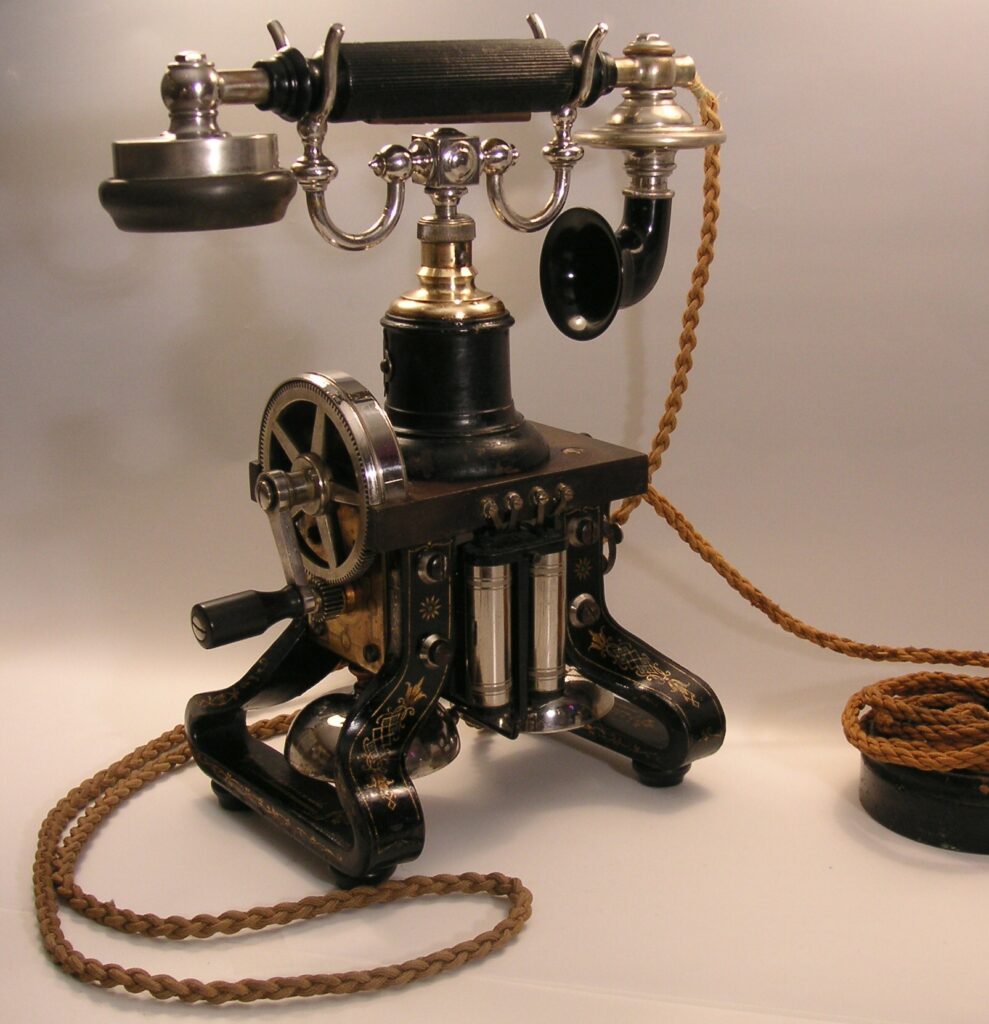

Either way, Ericsson’s telephone led to the first public telephone exchange in the world, opening in Stockholm in 1877.
In 1878, the first long-distance call was made between Stockholm and Gothenburg.
Today, Sweden is still one of the world’s leading countries in telecommunications with Lars’ company Ericsson till being at the forefront of mobile phone technology.
STDMA and Automated Identification System (AIS)
Here’s another invention from Håkan Lans, who also developed a system for transmitting data between multiple different transmitters and receivers in 1996 that he called Self-organized Time-Division Multiple Access (or STDMA).
The global AIS standard used on ships today is based on this Swedish time-slot method, STDMA, developed in the 1980s and 1990s.
That Swedish contribution is what makes it possible for thousands of ships to continuously broadcast their position without talking over each other.
After being developed in Sweden, the Swedish Maritime Administration worked internationally to establish it as a global standard.

And it’s not just boats that utilise AIS, NASA has found a particularly interesting use-case for it as well.
In the video below, NASA and the International Space Station demonstrates how a space-based radio receiver can track a ship’s Automatic Identification System (AIS) signal:
AIS has been particularly useful in crowded areas like the Baltic Sea, where there are a lot of ships travelling in close quarters.
The Three-Phase Electric Power System
The three-phase electric system was independently invented by as many as six inventors in the late 1880s (including Nikola Tesla in 1887), but Swedish inventor Johan Wenström’s solution had several advantages over those of his competitors. It was also the only one that was initially a complete system with generator, transformer and motor.

Wenström also said the following regarding Thomas Edison’s lightbulb (surely part of the reason he’s nicknamed “the Swedish Edison”):
Edison’s new invention of electric light: a glowing carbon strip, is the same thing that I discovered a year ago … If I had his laboratory, and resources, I would have done the same and better … a graphite strip between two mica plates provide a more effective light than Edison’s
Johan Wenström
Electric power today is transmitted either using a single-phase or a three-phase system. The three-phase system uses three wires, each carrying a different phase of the current. The phases are offset from each other by one-third of a cycle, so that the voltage waveforms produced by the three phases add up to produce a constant overall voltage.

The most common power supply in residential properties is a single-phase supply, while most industrial and commercial facilities procure electrical energy using a three-phase supply. One of the biggest differences between single-phase and three-phase supply is that it can accommodate higher loads.
Skype
In 2003, Skype was founded in Tallinn, Estonia by Niklas Zennström, from Sweden, and Janus Friis, from Denmark. The company was Swedish, but it’s important to note that it was also developed by four Estonian software engineers.
For the first time in history, it allowed people to communicate smoothly with each other over the Internet by voice, video, and instant messaging.
It also quickly became the choice for international calls because it was significantly cheaper than traditional long-distance phone services.
Skype became an instant worldwide success, and was quickly scooped up by American eBay for $2.6 billion USD in 2005, and later Microsoft for $8.5 billion USD.
Microsoft eventually integrated Skype in its operating system Windows, and used its technology as a basis for its Teams business communication software.

Skype not only became one of the most popular communication tools in the world, it also revolutionized the way we stay connected with loved ones who are far away and paved the way for popular newcomers such as Zoom and Apple’s FaceTime.
As of May 5, 2025, Skype (excluding Skype for Business) has officially been retired by Microsoft, and the technology fully baked into their other products.
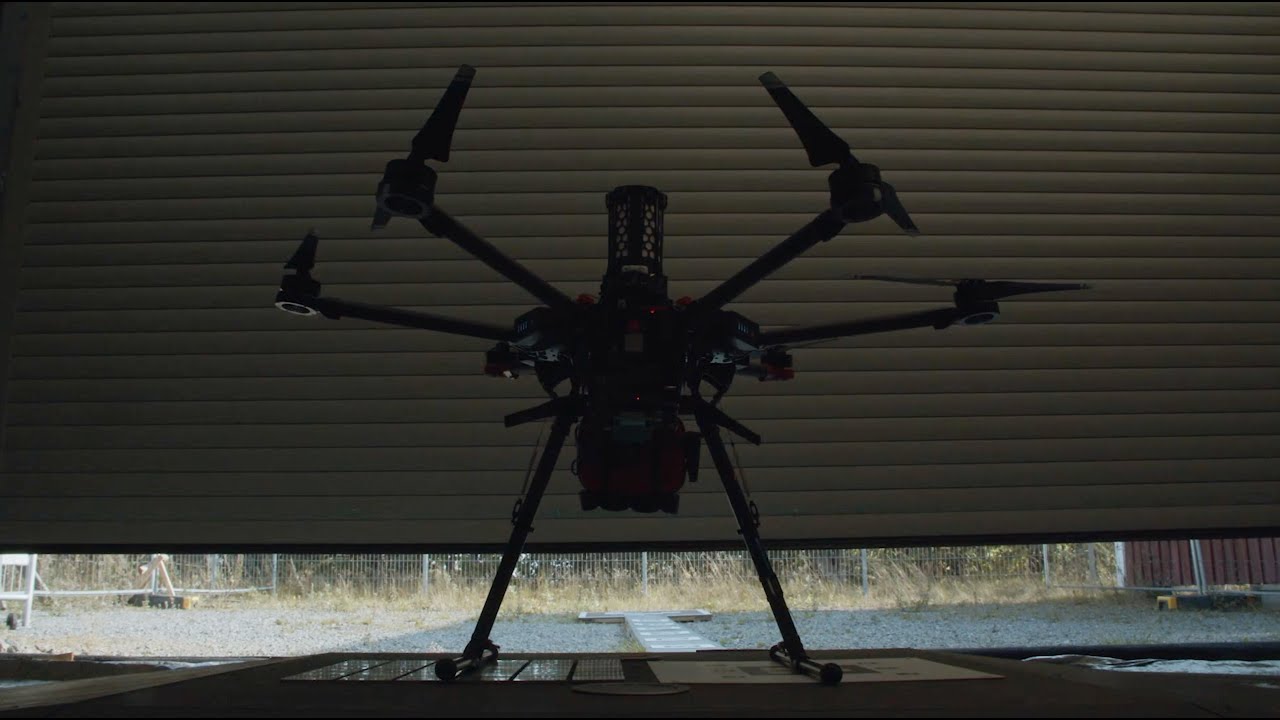
Life-saving Drones
Swedish innovators have come up with a number of life-saving drones, including the world’s first drone system that delivers an Automated External Defibrillator (AED) to heart-attack victims.
The first use of this drone took place in Trollhättan, Sweden in December of 2021, with an Everdrone autonomous drone delivering a defibrillator that saved the life of a 71-year-old Swedish man.
Everdrone AB mainly develops technology for drones and offers advanced drone services. The company is based in Gothenburg, Sweden.
Safety Matches
When it comes to safety matches, you can thank a Swede for your ability to light a fire without fear of singeing your fingers.
In 1844, chemist Gustaf Erik Pasch patented the red phosphorus match, which was much safer than the previous white phosphorus version.

Before Pasch’s invention, the highly poisonous white phosphorus was the key ingredient in matches, and workers in match factories frequently developed “phossy jaw,” a painful and often fatal condition caused by exposure to white phosphorus.
Despite Pasch’s innovative solution, the safety match didn’t became a commercial success until Jönköping brothers John Edvard and Carl Frans Lundström improved on the Pasch design a decade later, around 1855–60.

Safety matches quickly became one of Sweden’s main exports, and became synonymous with Jönköping around the world, well into the 20th century.
Alkaline Rechargeable Batteries
Rechargeable batteries as a concept date back to the French physicist Gaston Planté, who invented the lead-acid rechargeable battery in 1859.
Swedish engineer Ernst Waldemar Jungner then took rechargeable technology a big step further. In 1899 he developed the first practical nickel–iron (NiFe) and nickel–cadmium (NiCd) batteries, and later silver–cadmium (AgCd) cells. These higher-energy, more rugged batteries were widely used in everything from early submarines to portable tools.
Jungner’s batteries were notoriously reliable and durable, and were the only ones that could be used on Umberto Nobile’s dangerous North Pole expedition in 1928.
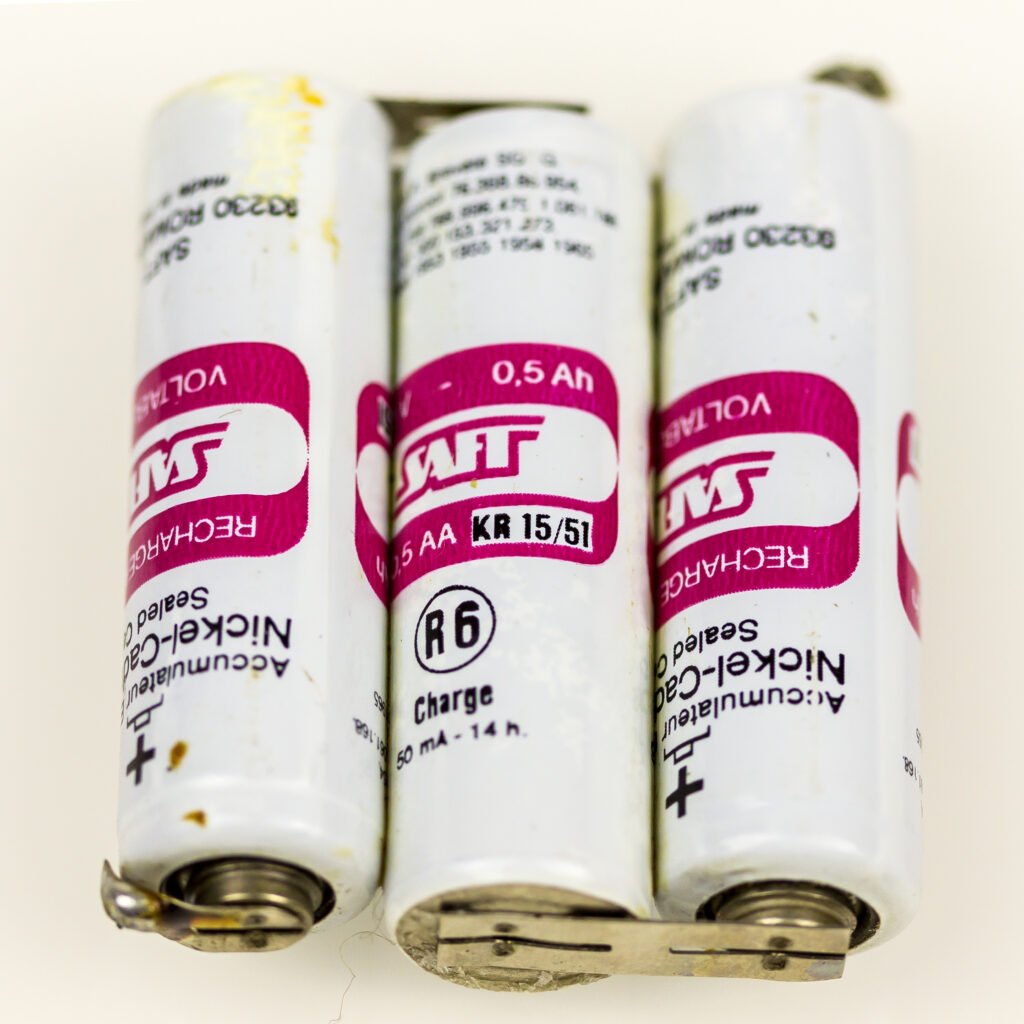

Many of Jungner’s original battery technologies were produced and distributed around the globe up until the 1970s, and Jungner’s company Saft AB is still making batteries in Sweden to this day.
The Gamma Knife
The Gamma Knife is a Swedish invention developed by Professor Lars Leksell at Karolinska Hospital, and is used to treat brain tumors. Leksell was active at Karolinska Hospital from 1960 to 1974, and the first Gamma Knife unit began treating patients in 1968.
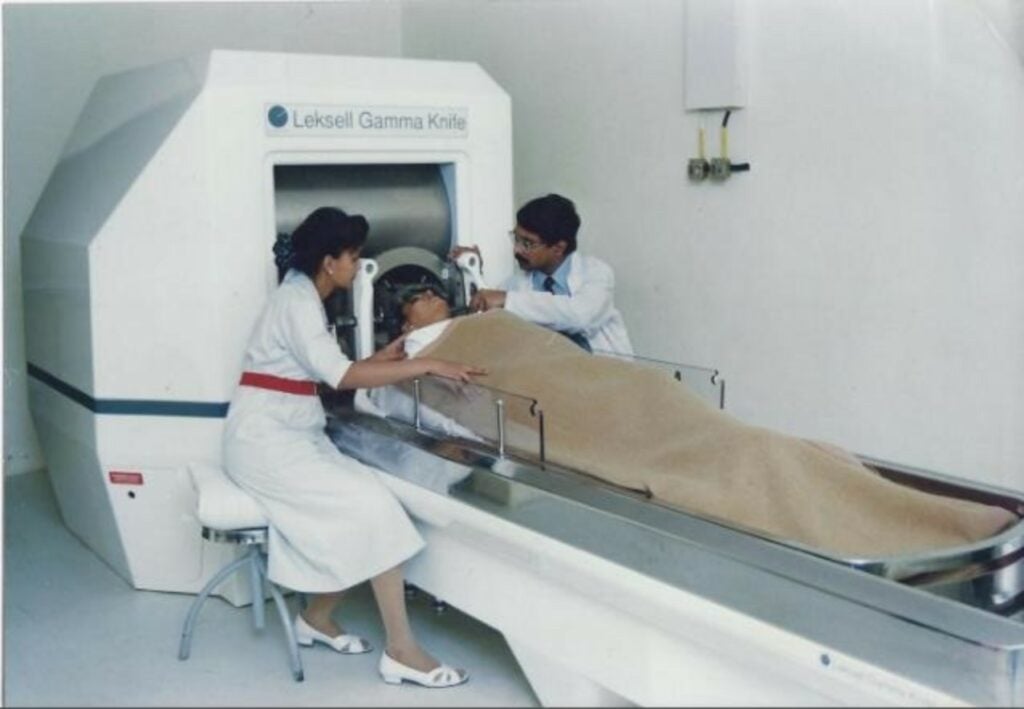
The device is able to target high doses of radiation to small areas of the brain without harming surrounding tissue.
Gamma Knife has been used to treat over 100,000 patients worldwide and is considered one of the most effective treatments for brain tumors.
ICU Ventilators
The ventilator was an evolution of the earlier iron lung, and in 1950, Swedish physician Carl Gunnar Engström designed one of the first modern electromechanical ICU ventilators (called the Engstrom Universal Respirator) which had a great impact and was mass-produced from 1954.
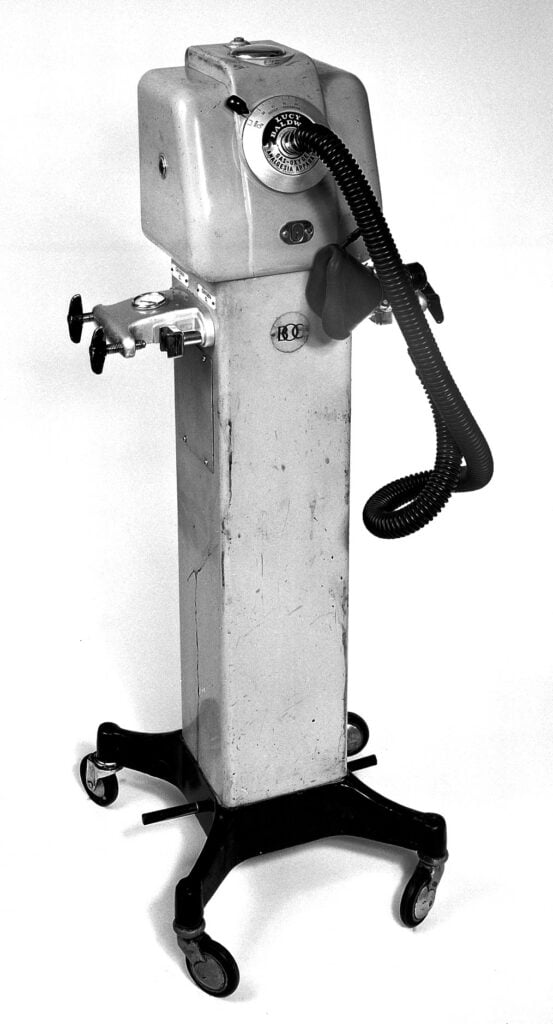

Engström’s ventilator was designed to treat those who suffered from respiratory paralysis due to polio, and was entirely mechanical.
By using flow control and volume measurement, several people, including Björn Jonson, Sven Ingelstedt, Georgios Psaros, and anaesthesiologist Lars Nordström, made significant contributions to the development of the so-called ServoVentilator around 1970.
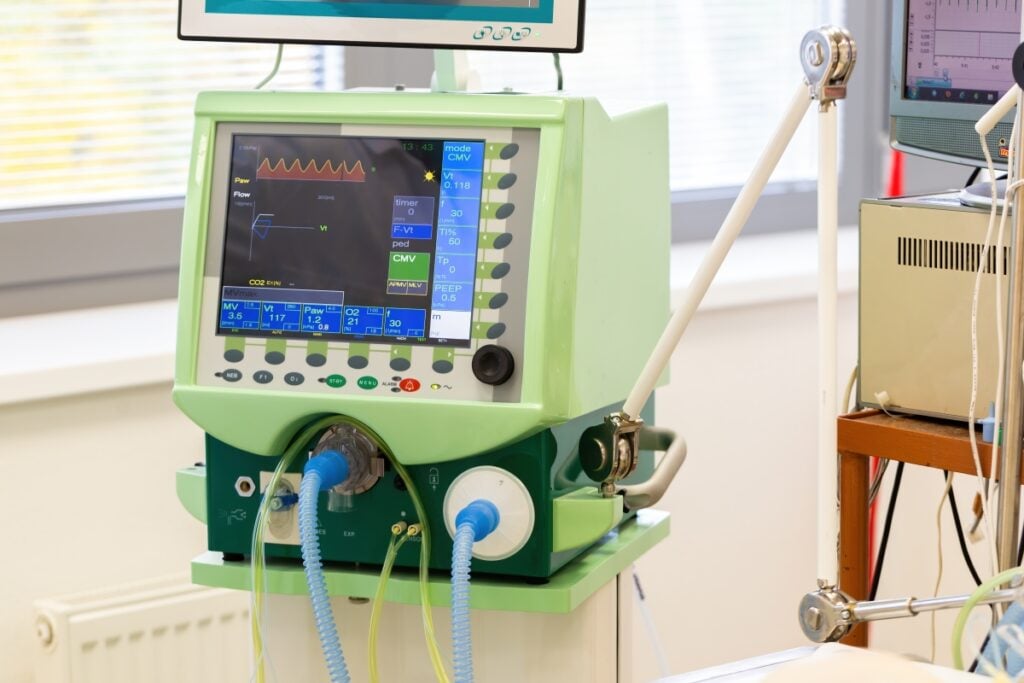
This new version not only supported the patient’s breathing according to their needs, but also provided measurements that could be used to diagnose and monitor the patient’s breathing problems, thus contributing to the development of the first specialized intensive care units (ICUs).
Tetra Pak Food Packaging
The Tetra Pak company was built on Erik Wallenberg’s ingenious innovation, a tetrahedron-shaped plastic-coated paper carton (Tetra Classic) that could hold milk without leaking, and did not cost much to produce.

Tetra Pak is today the world’s largest food packing company, with over 22,000 employees and sales in more than 170 countries.
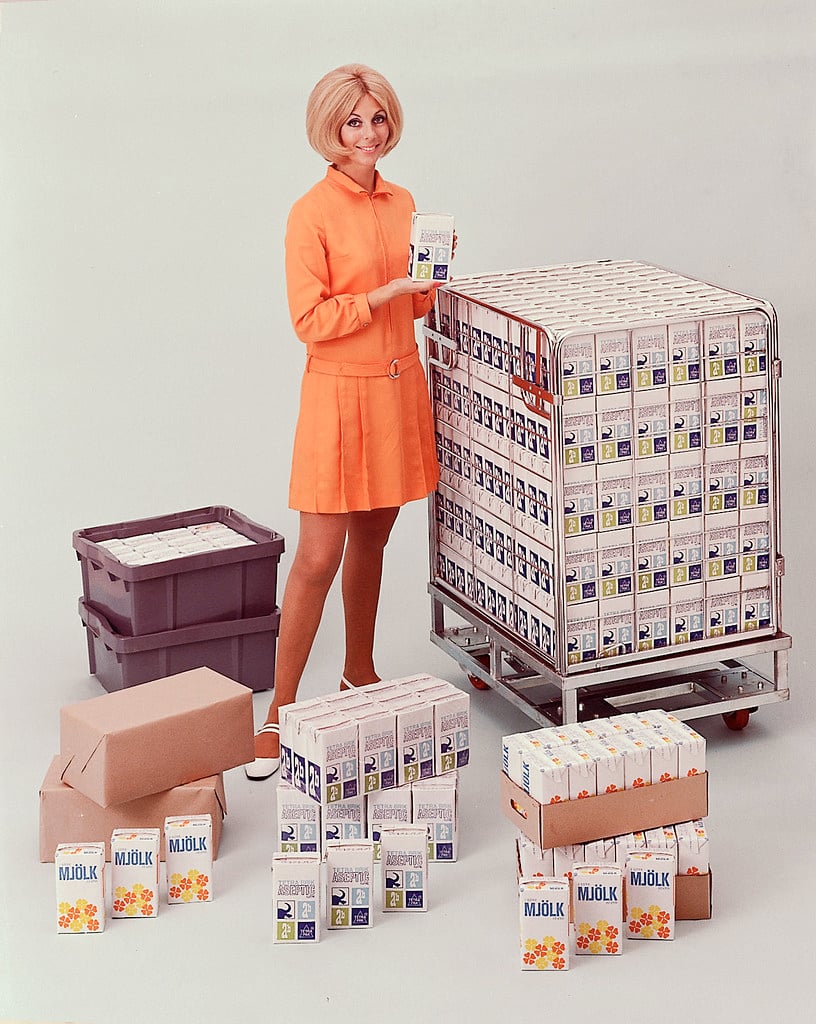

Another of the company’s signature products is the Tetra Brik, a rectangular paperboard box with a plastic liner that was introduced in 1952.

In addition to food packaging, Tetra Pak also provides food processing equipment and services. The company’s products are used in dairy, cheese, ice cream, beverage, and prepared food factories around the world.
Spotify and On-Demand Music Streaming
Before Spotify, there were earlier experiments with online music services and internet radio. What Spotify nailed – starting from Sweden in the late 2000s – was a legal, on-demand, all-you-can-listen streaming model that became truly mainstream.
The service was founded by Daniel Ek and Martin Lorentzon in 2006 in Stockholm, Sweden. The company’s mission is to “unlock the potential of human creativity by giving a billion creative artists the opportunity to live off their art.”

The founders’ initial idea was for Spotify to be free and funded by advertising, but after trying to tie up deals with the record companies, they were steered towards a subscription model on top of the freemium version. After 2.5 years of negotiations with record labels, Ek and Lorentzon launched Spotify in early November 2008.
Spotify had 281 million premium subscribers and 713 monthly users worldwide as of September 2025.
Here’s a cool video explaining how Spotify is changing the world of music forever:
The company’s freemium service allows users to listen to music for free with advertisements, and its premium subscription removes advertisements and allows users to listen offline as well. Spotify pays royalties to artists based on the number of streams their songs receive.
Though there is no denying Spotify’s impact on how we consume music today, the company has received significant criticism over the years, including by artists and producers for unfair compensation practices that often undermine the music creators, and by investigative journalists for including “fake” and AI artists in Spotify’s playlists to avoid paying out royalties to real artists.
In 2025, Spotify came under new scrutiny for running ICE recruitment ads on their platform on behalf of the US goverment, a decision they ultimately defended – leading to many users and artists calling for a complete boycott.
Gauge Blocks
If you’ve ever trusted a caliper, micrometer or precision machine tool, you’ve indirectly relied on a Swedish invention: gauge blocks, also known as “Jo blocks”.

In the late 1800s, Swedish engineer Carl Edvard Johansson invented a set of ultra-precise metal blocks that could be “wrung” together to build up exact lengths. His 1901 patent for a “gauge block set for precision measurement” became the basis for length calibration in modern industry.
Gauge blocks let factories everywhere mass-produce interchangeable parts – from engines to weapons – with a precision that simply wasn’t possible before. Johansson’s company CE Johansson AB sold these sets worldwide, and for a long time there was no other firm in the world that could match their accuracy.
The familiar steel tape measure itself was patented much earlier, in 1829, by British metalworker James Chesterman.
Medical Ultrasound and Echocardiography
Born in Germany, Hellmuth Hertz (whose grandfather Heinrich gave name to the Hertz frequency unit) eventually ended up studying physics at Lund University, where he met Inge Edler (born in nearby Burlöv, Sweden).
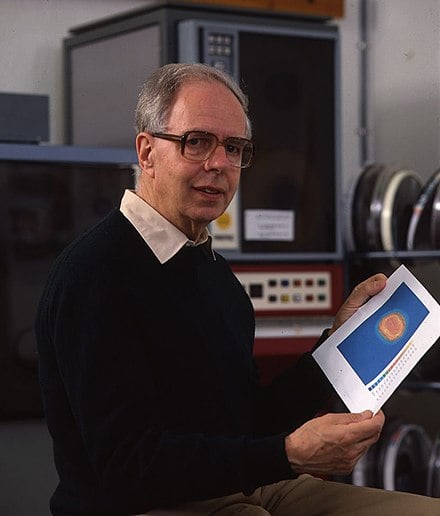
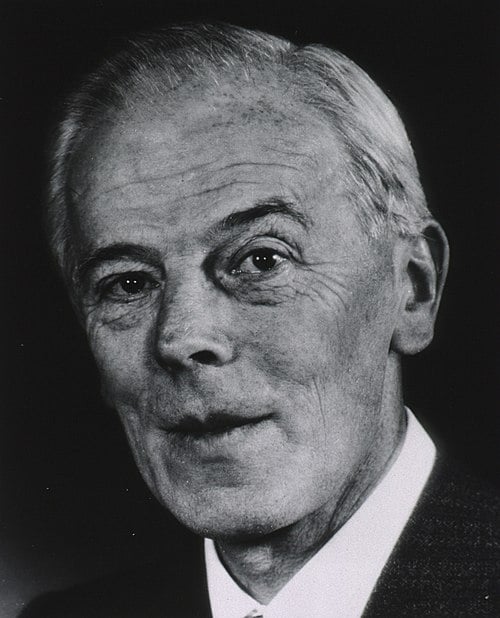


They would together end up making discoveries within the use of ultrasound that would have a phenomenal impact on the world of medicine.
Their work in Lund in 1953 produced the first recorded ultrasound echo from the human heart and laid the foundation for modern echocardiography.
One of the most important is undoubtedly inventing a way to utilize ultrasound waves to look into the human body (it had previously only been used to discover the damage in ships), which led them to also effectively establish the field of echocardiography (i.e. ultrasound of the heart) in 1953.
Since ultrasound was mainly used in ship repair at the time, the two inventors borrowed a device from the famous Malmö shipyard Kockums (my dad worked there for 12 years when I was younger!) to apply on the human body instead.
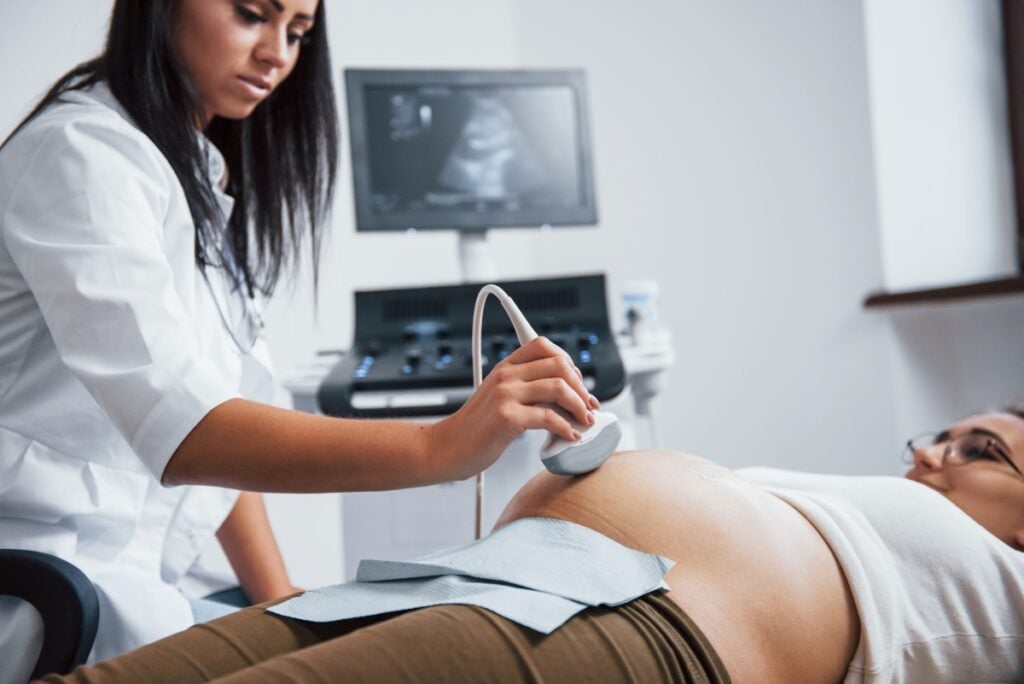
They would develop methods to use ultrasound to diagnose injuries inside the human brain and heart, and the method is still used to this day to measure development of foetuses among many other things.
The Multi-directional Impact Protection System (MIPS) Helmet
The story of MIPS begins in the late 1990s with Hans von Holst, a neurosurgeon, and Peter Halldin, a researcher at the Royal Institute of Technology in Sweden.
They recognized that traditional helmets were designed to absorb direct impacts but did little to mitigate the rotational motion that often accompanies head injuries. The brain is more sensitive to rotational forces than direct impacts, making this an area of critical concern for helmet design.
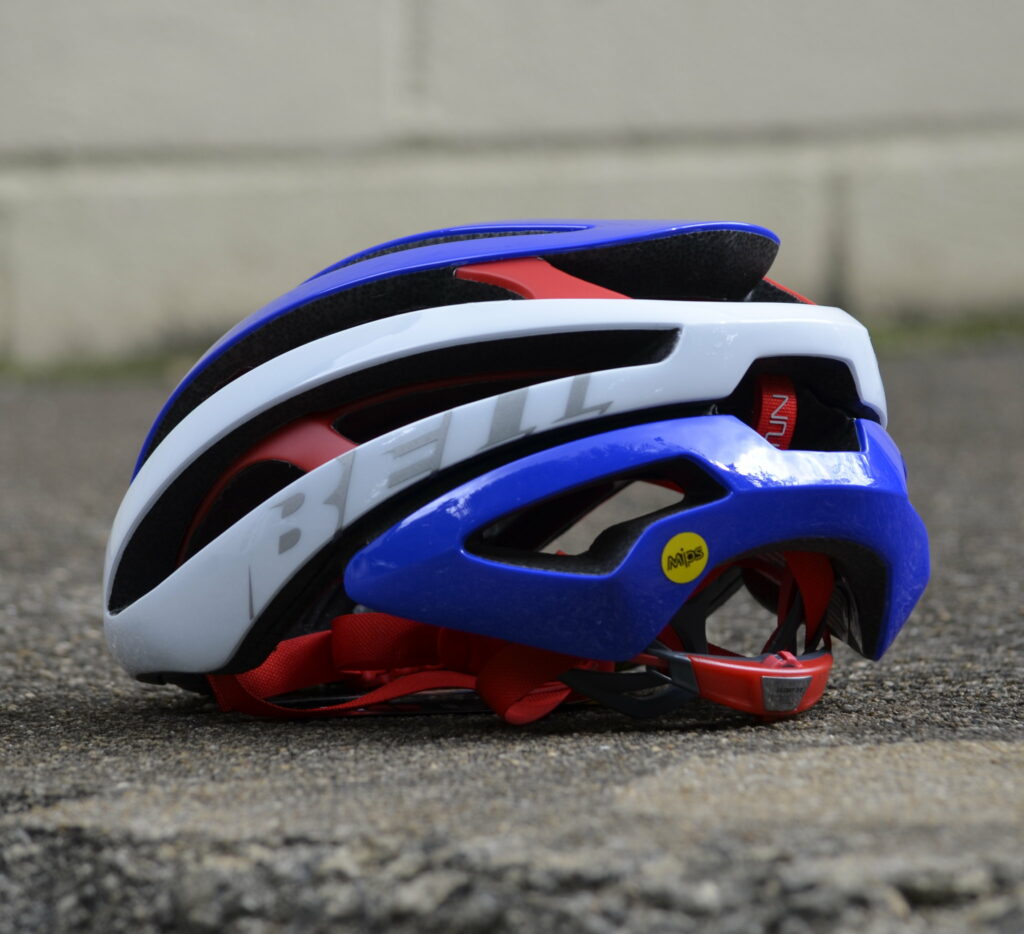

The core concept behind MIPS is a low-friction layer inside the helmet that allows the outer shell to rotate slightly relative to the head upon impact. This ingenious design mimics the brain’s own protection system—a layer of cerebrospinal fluid that allows the brain to move slightly within the skull, thereby reducing the rotational force transferred to it.

Register Mips Helmet
The implementation of MIPS technology marked a significant leap forward in helmet safety, and its applications span across numerous sports and activities, including cycling, skiing, motorcycling, and equestrian sports, where helmets are a critical component of safety gear.

Triple Eight Gotham Dual MIPS Skateboard & Bike Helmet
The technology’s seemingly fast adoption by leading helmet manufacturers worldwide is a testament to its effectiveness in reducing brain injuries.
Lidocaine (Local Anesthetic)
Lidocaine is a medication used to numb tissue in a specific area. It is a local anesthetic and works by temporarily blocking the nerves that send pain signals to the brain.
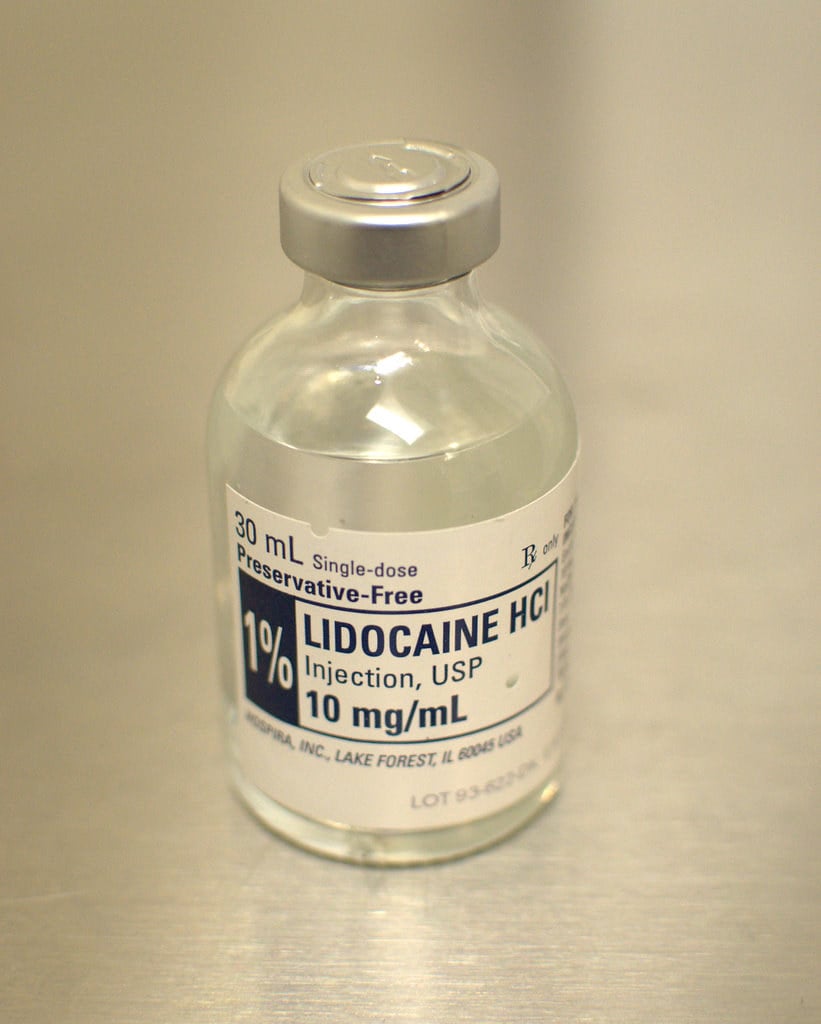
Lidocaine was first synthesized in Sweden in 1943 by Nils Löfgren and Bengt Lundqvist, and is now used worldwide for a variety of purposes, including as a numbing agent during medical procedures (it is especially popular in dentistry).
Oat-Based Drinks
Oat-based drinks have been around in Sweden since the early 1900s, in the form of a very popular Swedish drink called Välling that pretty much makes small kids magically sleep through the night.
But it wasn’t until the 1990s a completely dairy-free oat drink started gaining popularity, as a plant-based alternative to regular milk.
The biggest producer by far is Oatly (based in Landskrona, Sweden, not too far away from where I live), who make products such as the immensely popular iKaffe (without a doubt the favorite coffee companion in our household since it was introduced).

Oat milk is a dairy-free alternative to cow’s milk and is made from oats that have been soaked and blended with water. It has a creamy texture and a slightly sweet taste, which I find perfect as a complement to coffee (instead of milk or cream).

Oatly Oat Milk, Variety Pack, 32oz, Pack of 6
No added sugar, dairy, soy, nuts, thickeners, gums, or GMOs. View Price
It is a good source of vitamins and minerals (including calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium), low in fat, and cholesterol-free.
The Re-washable Dishcloth
The rewashable Wettex dishcloth was invented in 1949 by Curt Lindquist. It can absorb up to 15 times its own weight in liquids, and is made of a material consisting of regenerated cellulose reinforced with cotton fibre.

The material used allows it to be washed over and over again, without losing its shape or quality. All you have to do is wipe, squeeze out the liquid, and give it a quick rinse. This makes it environmentally friendly, on top of being very effective.

Wettex dishcloths are nowadays available in more than 50 countries worldwide, and produces more than 220 million units a year in the original Norrköping factory form the 1940s.

Wettex 10-Pack of Swedish Dishcloths
As a side note, Wettex now goes under the name Freundeberg Household Products.
Abstract Paintings
Swedish artist Hilma af Klint created large, fully abstract works as early as 1906 – years before Wassily Kandinsky, Mondrian and Malevich. Because many of these paintings remained hidden until the late 20th century, art history long credited others as “first,” but a growing number of art historians now argue that af Klint should be recognised as one of the very earliest pioneers – and possibly the first – of abstract painting.
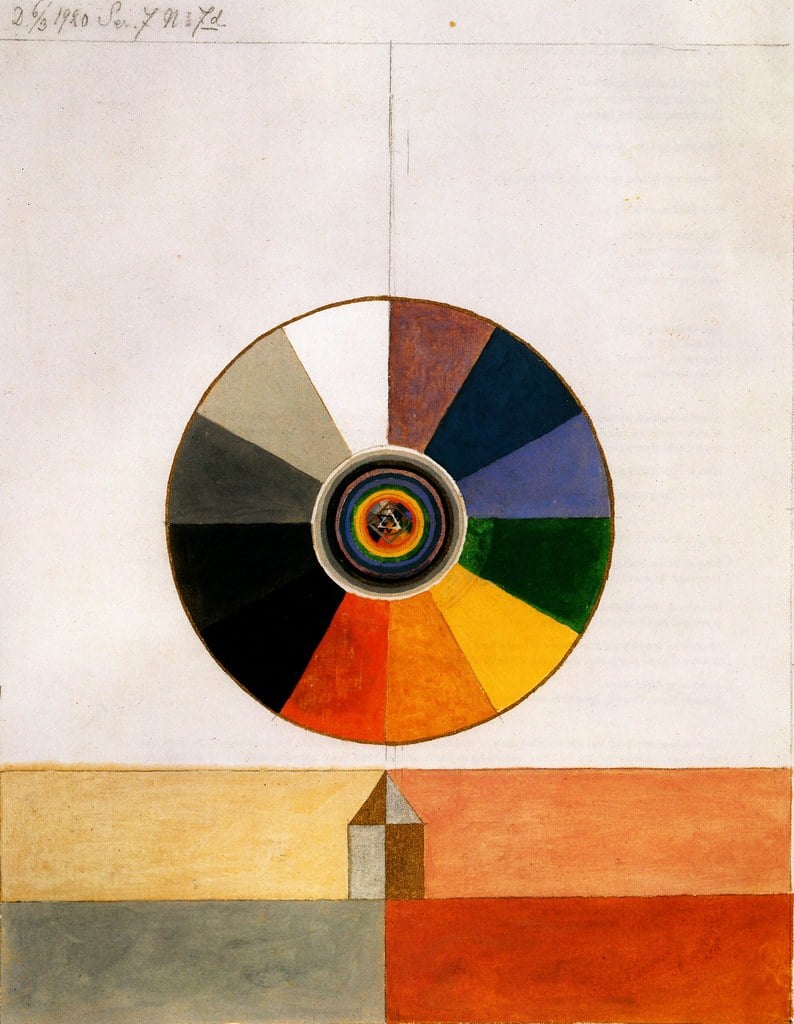
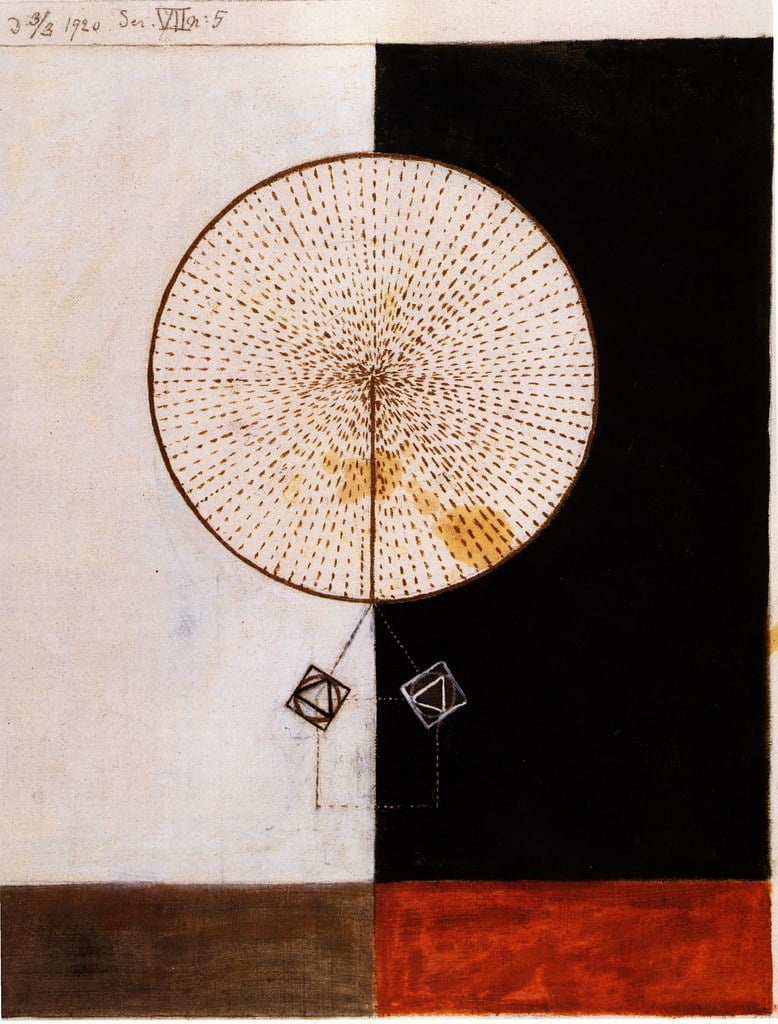

Her work was influenced by theosophy and spiritualism, and she believed that her paintings could be used to channel higher truths.
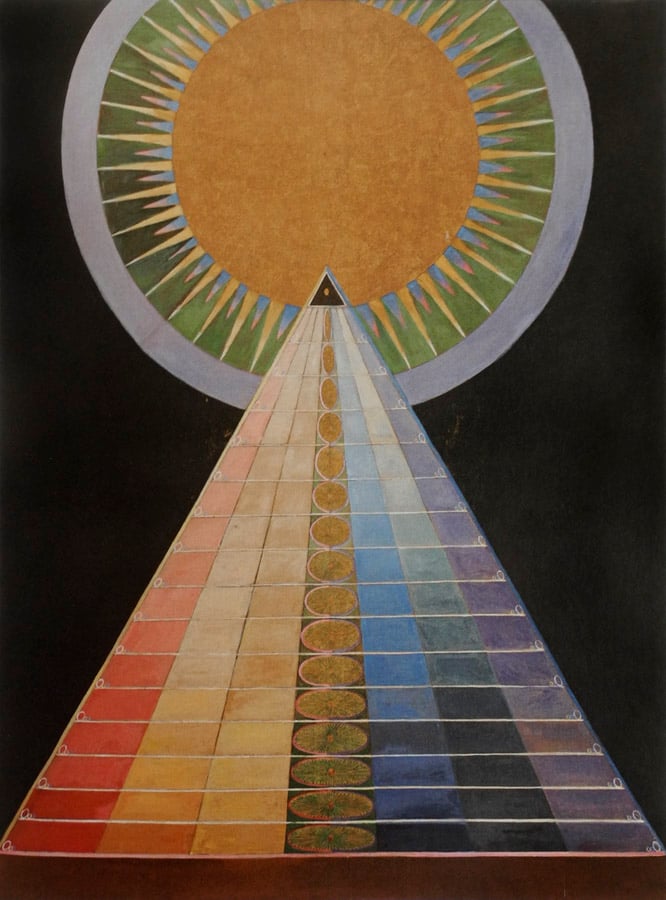

Af Klint died in 1944, but her work gained renewed interest in the 21st century, when it was exhibited at the Guggenheim Museum in New York City.
Flat-pack Furniture
When most people think of Swedish design, they think of IKEA – and behind that global flat-pack phenomenon stands a very concrete problem: furniture that was too bulky and expensive to ship.

In the mid‑1950s, IKEA designer and draughtsman Gillis Lundgren was trying to transport a table home for a catalogue shoot. It wouldn’t fit in his car, so he unscrewed the legs to make it easier to transport – and realised that customers could do the same. That simple idea evolved into the flat-pack, self-assembly concept that would transform how furniture is made, shipped, and sold worldwide.
IKEA wasn’t literally the first company ever to sell knock-down furniture, but Lundgren and his colleagues systematised flat-pack design at scale: designing products, packaging, and logistics together so furniture could ship in compact boxes, be moved by ordinary customers, and assembled at home with a simple instruction sheet and a few screws.
The impact is hard to overstate. Flat-pack furniture dramatically cut transport and storage costs, helped make modern furniture affordable for a far larger share of the global middle class, and inspired countless imitators. Today, the idea that you might pick up a table or a bed in a flat cardboard box and assemble it yourself feels completely normal – largely thanks to this Swedish design and logistics breakthrough.
The Milk-Cream Separator
Before the late 1800s, separating cream from milk was slow, manual work. Farmers would leave milk standing in shallow pans for hours (or overnight) and then skim the cream off the top by hand. It was labour-intensive, inconsistent, and not great for hygiene – especially as farms grew larger and milk volumes increased. Swedish engineer Gustaf de Laval figured there had to be a better way to do the same job using physics instead of patience.
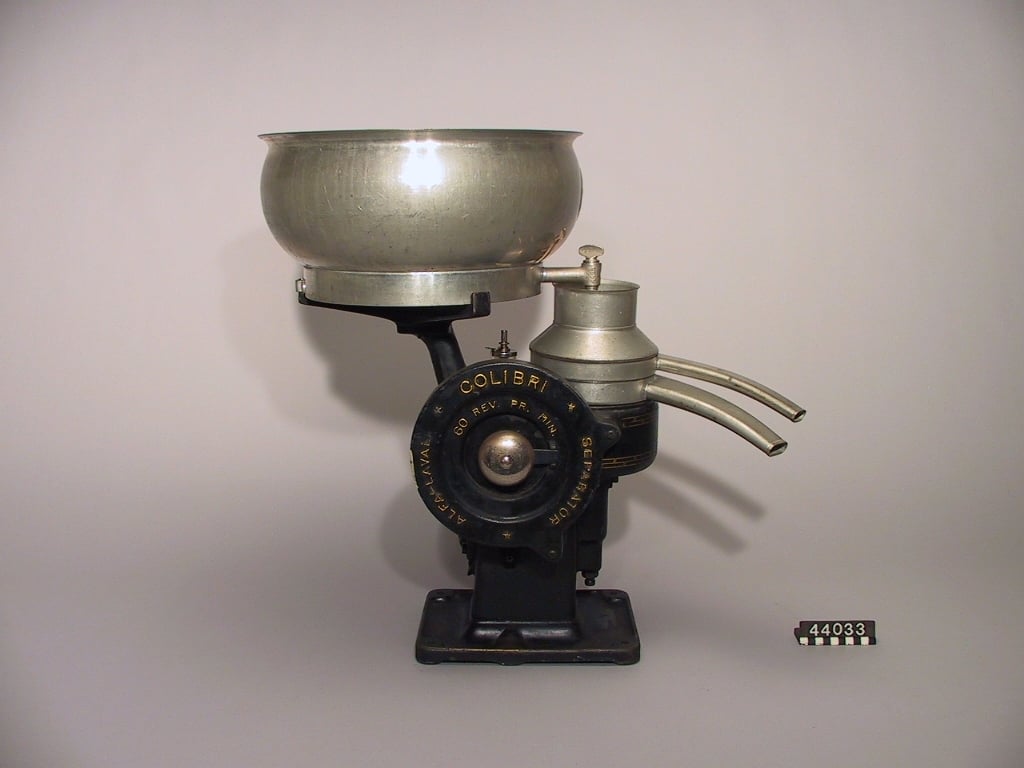

In 1878, de Laval and his business partner Oskar Lamm patented a centrifugal milk-cream separator: a spinning bowl that flings heavier skim milk outwards while the lighter cream stays closer to the centre, with two separate outlets for each. What used to take many hours by gravity could suddenly be done in minutes, with far less spoilage and a much more consistent fat content.
The invention took off. In 1883 they founded AB Separator in Stockholm (the company that later evolved into Alfa Laval and DeLaval) to manufacture the machines, and cream separators spread quickly through creameries across Europe and beyond. Mechanical separation helped kick-start the rise of large co-operative dairies in Sweden and neighbouring countries, and it rewired the economics of dairy farming by letting farmers process more milk, waste less cream, and standardise their products.
The same basic separator technology later turned up everywhere from yeast and beer production to engine-oil cleaning and modern food and pharma processes. So even if a cream separator doesn’t look as flashy as, say, a Spotify app or a Gamma Knife, it’s one of those quietly world-changing Swedish inventions that underpins a massive chunk of the global food industry.
Sources:
https://patents.google.com/patent/US3043625
https://www.media.volvocars.com/se/sv-se/media/pressreleases/18406
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/01.cir.0000016183.07898.90
https://www.nyteknik.se/digitalisering/hakan-lans-pustar-ut-efter-forlikning-6417598
https://www.networkworld.com/article/2307621/swedish-inventor-gets-day-in-court.html
https://www.ericsson.com/sv/om-oss
https://www.bbc.com/news/technology-59885656
https://new.abb.com/se/om-abb/kort/historik/abb-jonas-wenstrom
https://www.karolinska.se/en/karolinska-university-hospital/medical-areas/gamma-knife-surgery/
https://www.prv.se/sv/larare/uppfinnare-fran-sverige/curt-lindquist—wettextrasan/
https://www.artsy.net/article/artsy-editorial-first-abstract-artwork
https://www.ikea.com/ph/en/this-is-ikea/about-us/the-story-of-ikea-flatpacks-puba710ccb0/
https://www.guinnessworldrecords.com/world-records/107974-first-flatpack-furniture
https://www.tekniskamuseet.se/en/learn-more/swedish-inventors/gustaf-de-laval-milk-cream-separator/
https://www.alfalaval.com/about-us/history-of-alfa-laval/
https://books.google.com/books?id=a7nv0AEACAAJ
https://www.sec.gov/ix?doc=/Archives/edgar/data/1639920/000163992025000003/ck0001639920-20241231.htm
 Swedish Breakfast Habits: A Complete Guide
Swedish Breakfast Habits: A Complete Guide The 36 Best & Most Popular Swedish Chocolate Brands
The 36 Best & Most Popular Swedish Chocolate Brands Traditional Swedish Clothing: The National & Regional Folk Costumes of Sweden
Traditional Swedish Clothing: The National & Regional Folk Costumes of Sweden The 44 Best Scandinavian Outdoor Clothing Brands
The 44 Best Scandinavian Outdoor Clothing Brands











Typical Swede, taking credit for other’s works. Won’t go through every item, but here’s a few: Zipper inventor: Whitcomb Judson, American; monkey wrench, Loriing Coes, American; Rechargeable battery, Gaston Plante, France; pace maker, John Hopps, Canada. Sweden primary contribution has been proving Nazi Germany with steel and iron ore to allow the Germans to kill millions of people.
Hello David,
First off, thanks for reading and taking the time to comment! I always appreciate when readers chime in with their perspectives as it helps keep articles factual and balanced – which I always aim for.
You’re definitely correct that some of these inventions have a longer backstory than “one person in one country did everything,” so let me clarify a few of the examples you brought up:
Zipper – Elias Howe and later Whitcomb Judson did indeed patent zipper-like fasteners in the 19th century, but the reason I attribute the zipper invention to Gideon Sundbäck is that he designed the modern, reliable zipper and the production method that finally made zippers practical and widely used. I’ve updated the wording to say “modern zipper” and to mention the earlier American patents explicitly to avoid any confusion.
Adjustable wrench / monkey wrench – Loring Coes absolutely deserves credit for what Americans call the classic “monkey wrench.” Johan Petter Johansson’s contribution is different: he invented the modern adjustable spanner and a Swedish-style adjustable pipe wrench that became global standards through Bahco. I’ve reworded that section so it no longer sounds like Johansson invented Coes’ monkey wrench.
Rechargeable batteries – Gaston Planté did invent the first rechargeable lead–acid battery in France in the 1850s. The Swedish contribution I’m highlighting is Waldemar Jungner’s later invention of practical alkaline rechargeable systems (NiFe, NiCd, AgCd), which solved different technical problems and ended up in things like submarines and tools. I’ve changed the heading to “Alkaline rechargeable batteries” and added a clear nod to Planté.
Pacemaker – John Hopps in Canada and others worked on early external pacemakers. The Swedish team of Rune Elmqvist and Åke Senning then built and implanted the first fully implantable pacemaker in 1958. My original wording just said “first pacemaker,” which I agree is too sloppy. I’ve reworded that to “first implantable pacemaker” and now mention the external devices that came before to give credit where credit is due.
More broadly, what you’re pointing to is how invention credit usually works everywhere, not just in Sweden. We all do the same thing with some of the most famous “American” inventions. People say “Edison invented the light bulb” even though others had working lamps decades earlier – Edison’s version is the one that lasted long enough, was cheap enough, and came with a full electrical system, so history sticks his name on it. We talk about Bell as “the inventor of the telephone” even though Meucci and Reis were experimenting with voice transmission before him – Bell is remembered because his design worked reliably, was patented properly, and scaled into a real network. And lots of people still say “Apple invented the smartphone”, even though IBM’s Simon and early Nokias were there first; the iPhone is just the first version polished enough to redefine the category and go mainstream.
The pattern is usually: first wave proves an idea is possible, second wave nails the design and commercialization – and the second wave gets remembered as “the” inventor. The Swedish examples in my article (including the ones you brought up) sit in that same pattern: there are important non-Swedish precursors, and then a Swedish engineer or company comes along and creates the version that actually works, scales, and often becomes the global standard.
Finally, Sweden’s iron ore and ball bearing exports to Nazi Germany were absolutely significant and are a serious, uncomfortable part of Swedish history. That’s worth discussing, but it’s a different topic than whether, for example, the three-point seat belt, Tetra Pak, Gamma Knife, Spotify, etc. actually came out of Swedish engineers and companies. One does not cancel out the other.
If you see any other specific items in the list that you think are factually off, feel free to point to them and I’m happy to dig deeper and clarify if necessary. The goal isn’t to “steal” inventions from other countries or inventors – it’s to map out where (the very small country) Sweden has played a role in a much bigger, global innovation story.
–Karl