Most of the nations in modern-day Central, Western, and Northern Europe can be described as either Nordic, Germanic, or Celtic. But it’s definitely not easy keeping all of the different European ethnicities apart, especially not since many countries can feature elements of multiple ones!
So if you’re curious about the exact difference between Nordic, Germanic, and Celtic, and which countries, languages, and people are involved when speaking about these terms — you’ve come to the right place.
What’s the Difference Between Nordic, Germanic, and Celtic?
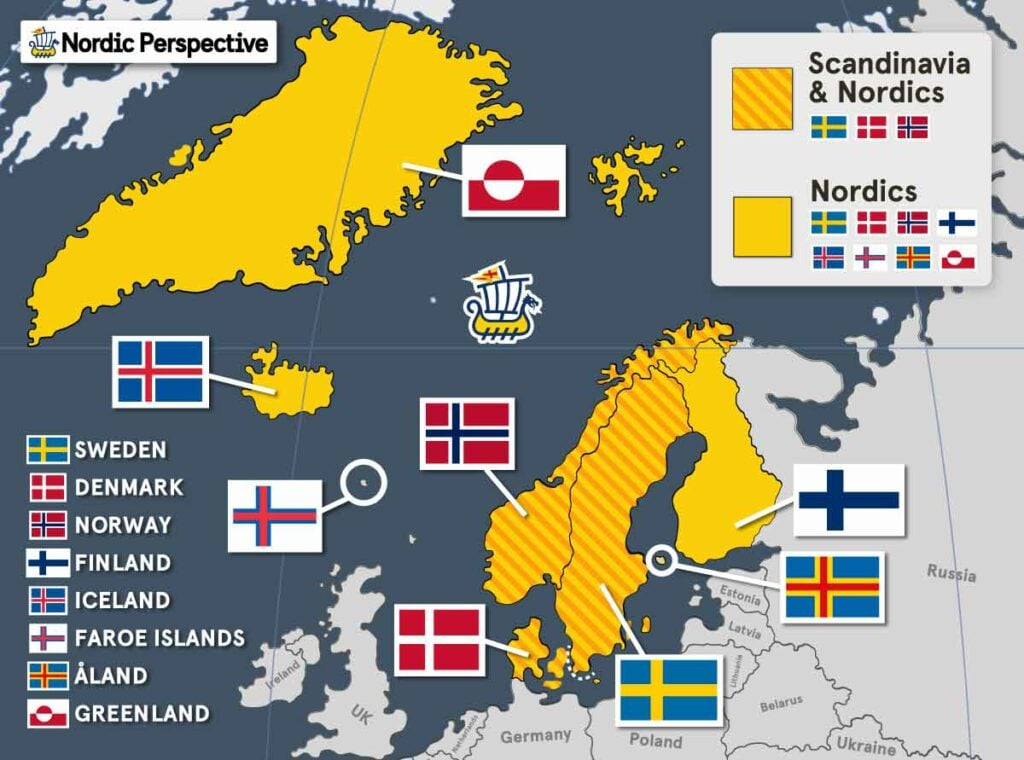
- Nordic = Relating to the Nordic people, languages, or cultures of Sweden, Denmark, Norway, Finland, Iceland, Faroe Islands, Åland, and Greenland (descendants of the Norse people and languages, i.e. the Vikings).
- Germanic = Relating to the Germanic people, languages, or cultures that originated from Southern Scandinavia and Northern Germany after the bronze age and today span across Northern and Central Europe in countries such as England, Germany, and the Netherlands.
- Celtic = Relating to the Celtic people, languages, or cultures that were present in most of Central and Western Europe after the bronze age, and in countries such as Ireland, Scotland, Wales (and to a certain extent France, Belgium, Switzerland, Austria and Italy) today.
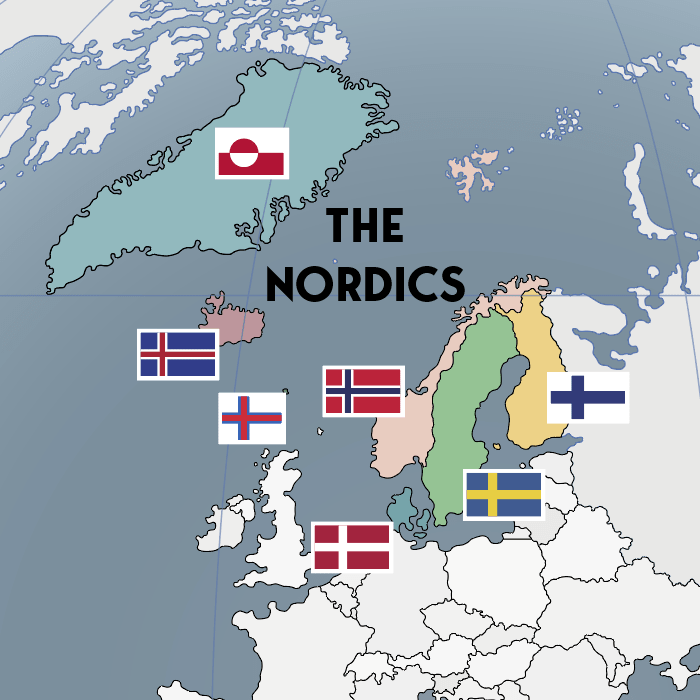
Nordic
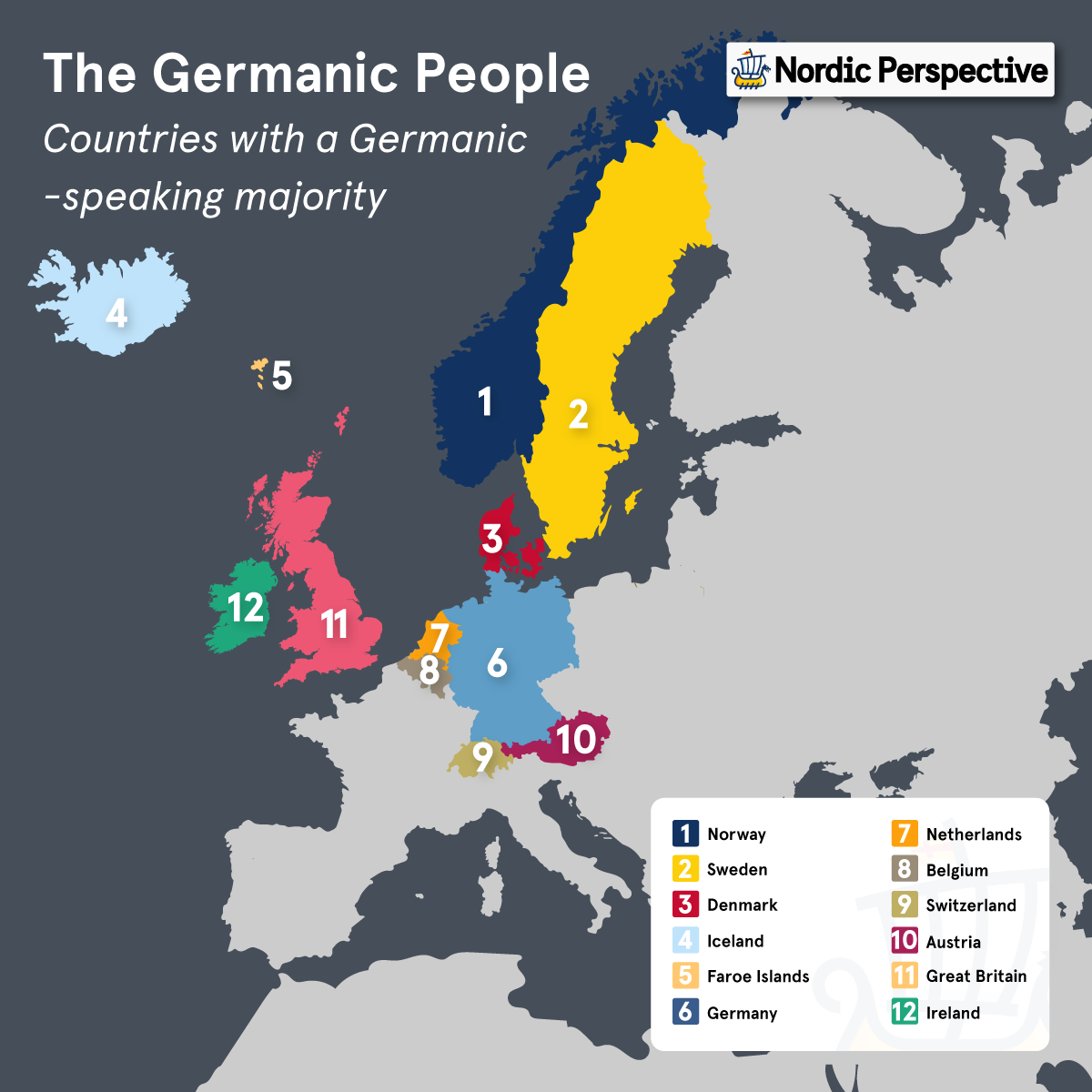
Germanic
🇧🇪, Austria 🇦🇹, Switzerland🇨🇭, Luxembourg 🇱🇺
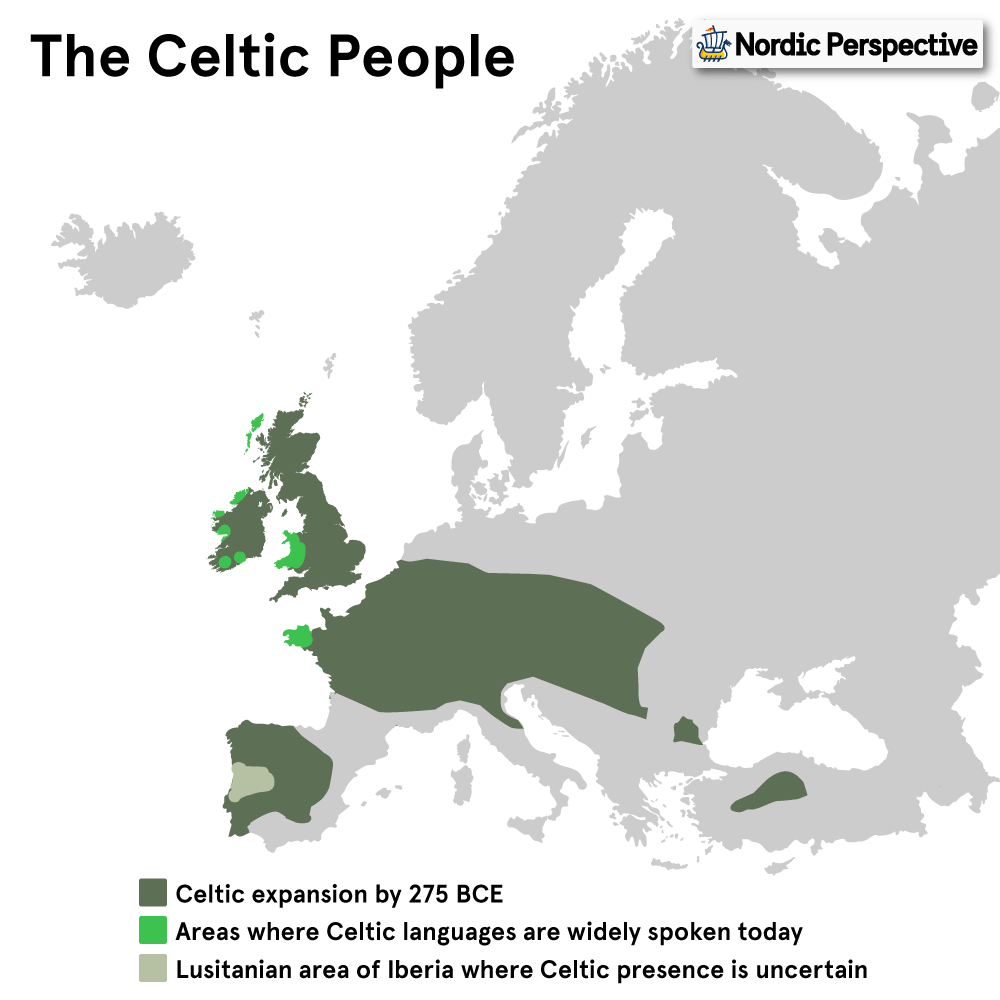
Celtic
(partly France
🇫🇷, Belgium
🇧🇪, Italy
🇮🇹, Austria 🇦🇹, Switzerland🇨🇭)
*Greenland speaks an Eskimo–Aleut language but is part of the Kingdom of Denmark, which is a Nordic country.
To sum it up in plain words, Nordic refers to anything relating to the Nordic languages & cultures (also called North Germanic), Germanic refers to anything relating to the Germanic languages & cultures, and Celtic refers to anything relating to the Celtic languages & cultures.
Location: Northern Europe
Combined Population: 27.38 million
Combined Total Area:
1 322 710 sq mi, across 5 timezones (US 50 states + D.C. = 3 796 742 sq mi across 6 timezones)
Nordic: The Northern European Region and Its People
The more modern term Nordic refers to citizens of or anything related to the Nordic (or North Germanic) countries in northern Europe (Sweden, Norway, Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Faroe Islands, Åland, and Greenland). This term has mainly been used since the establishment of Förening Norden (The Nordic Associations) in 1919.
The Nordic cross flag refers to the type of flags the Nordic countries have, containing a Nordic or Scandinavian Cross. The oldest of these is the Danish, dating back to 1219 according to legend.
Germanic: the Germanic Cultures & Languages
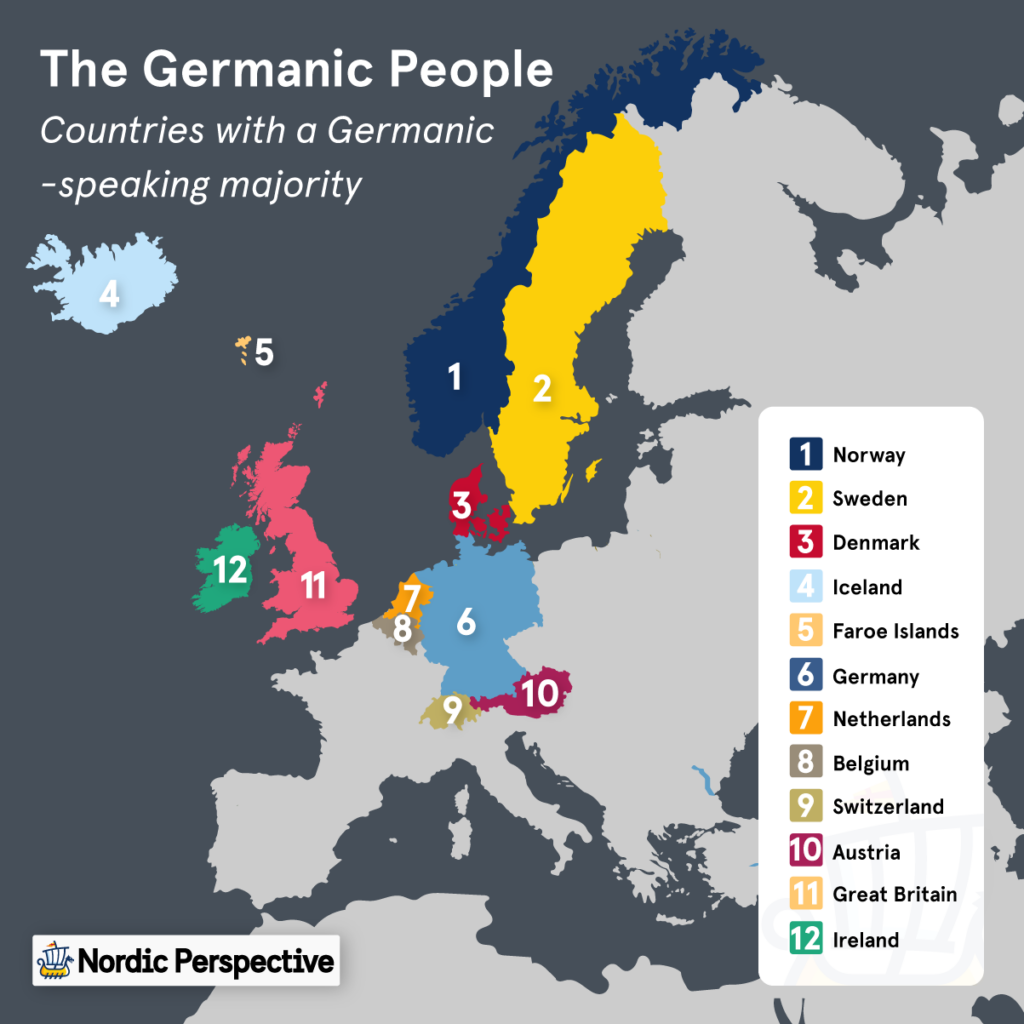
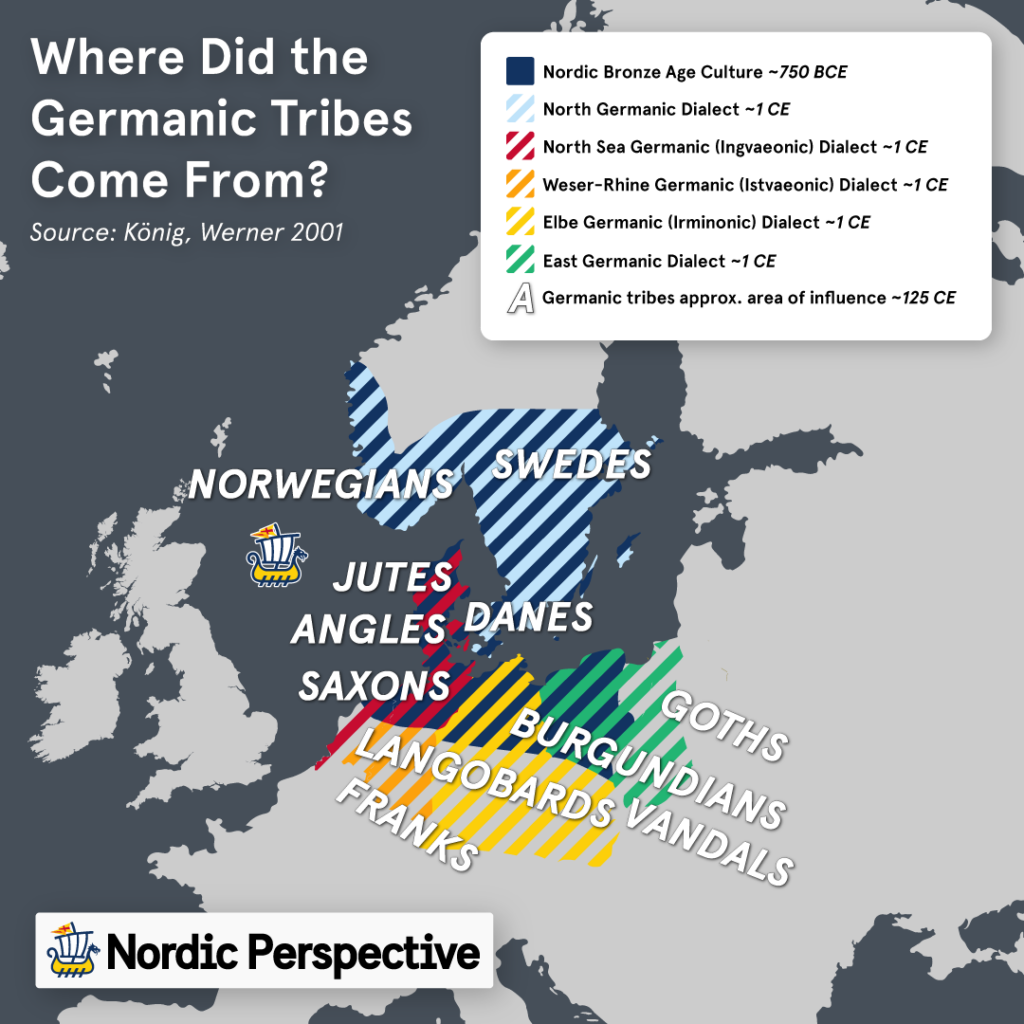
The Germanic tribes were groups of people originating from northern and central Europe during the Iron Age, sharing a common language group that is the root of all Germanic languages (which today includes over 515 million native speakers of languages like English, German, Dutch, and the Nordic languages to name a few).
To make things a bit more complicated, the Germanic people are all thought to have originated from a fairly small area in southern Scandinavia and northern Germany around the 4th century BCE, centered around the province of Scania, Sweden.
In other words, all Germanic languages and cultures mainly originated from the Nordic region, from where they would set out on the Great Migrations around all of Europe and parts of Asia that they would complete.
For more information about the Nordic and Germanic connection, go check out my article where I explain all the Scandinavian, Viking, and Germanic links.
Location: Central, Western & Northern Europe
Population Germanic Speaking Countries: 202 million
Native Germanic Speakers: 515 million
Combined Total Area: 720 379 sq mi, across 5 timezones (US 50 states + D.C. = 3 796 742 sq mi across 6 timezones)
Location: Central & Western Europe
Combined Population Native Celtic Speakers: 19.6 million
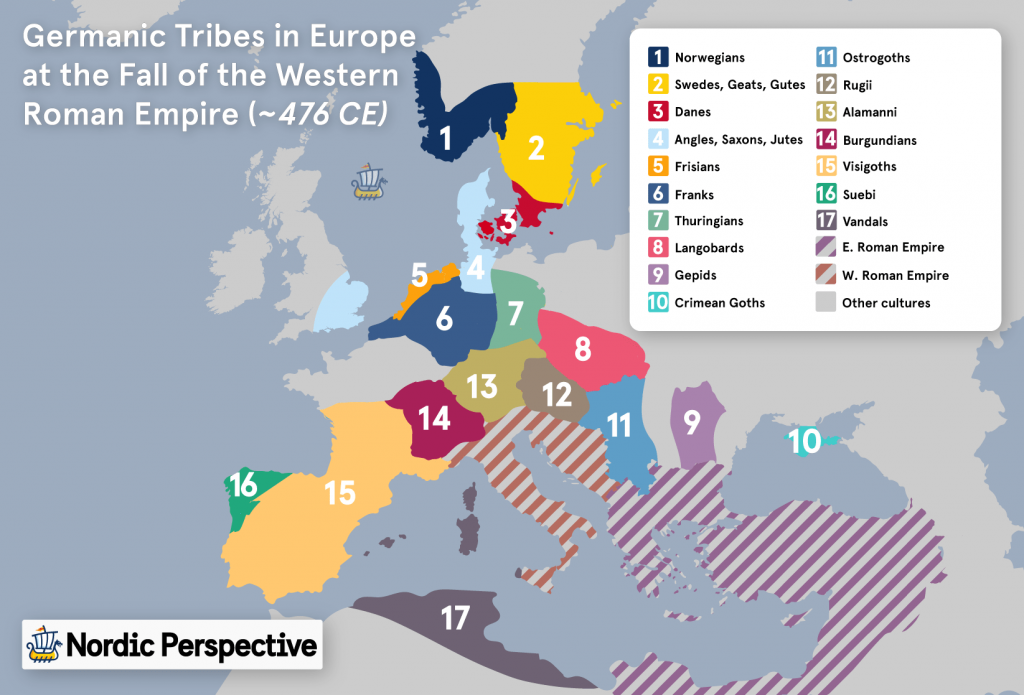
Celtic: The Celtic Cultures & Languages
The Celts were a collection of people who originated from central Europe, and ended up migrating through and inhabiting large parts of Europe during the Iron Age.
Around 275 BC the Celtic culture reached its largest influence, covering large parts of Central, Western, and Eastern Europe. After this point, the Celts would gradually be pushed back by Roman Legions from the south and Germanic tribes from the north.
Some of the more famous Celtic tribes include the Gauls (modern-day France), Britons (Britain), Galatians (Northern Spain), Belgi (Belgium), and Elveti (Switzerland).
The Celtic people ultimately intermingled with the Germanic and Roman people who came to dominate most of the places in Europe were Celtic influence gradually disappeared.
The only remaining Celtic nations today are Brittany, Ireland, Scotland, Wales, Isle of Man, and Cornwall.
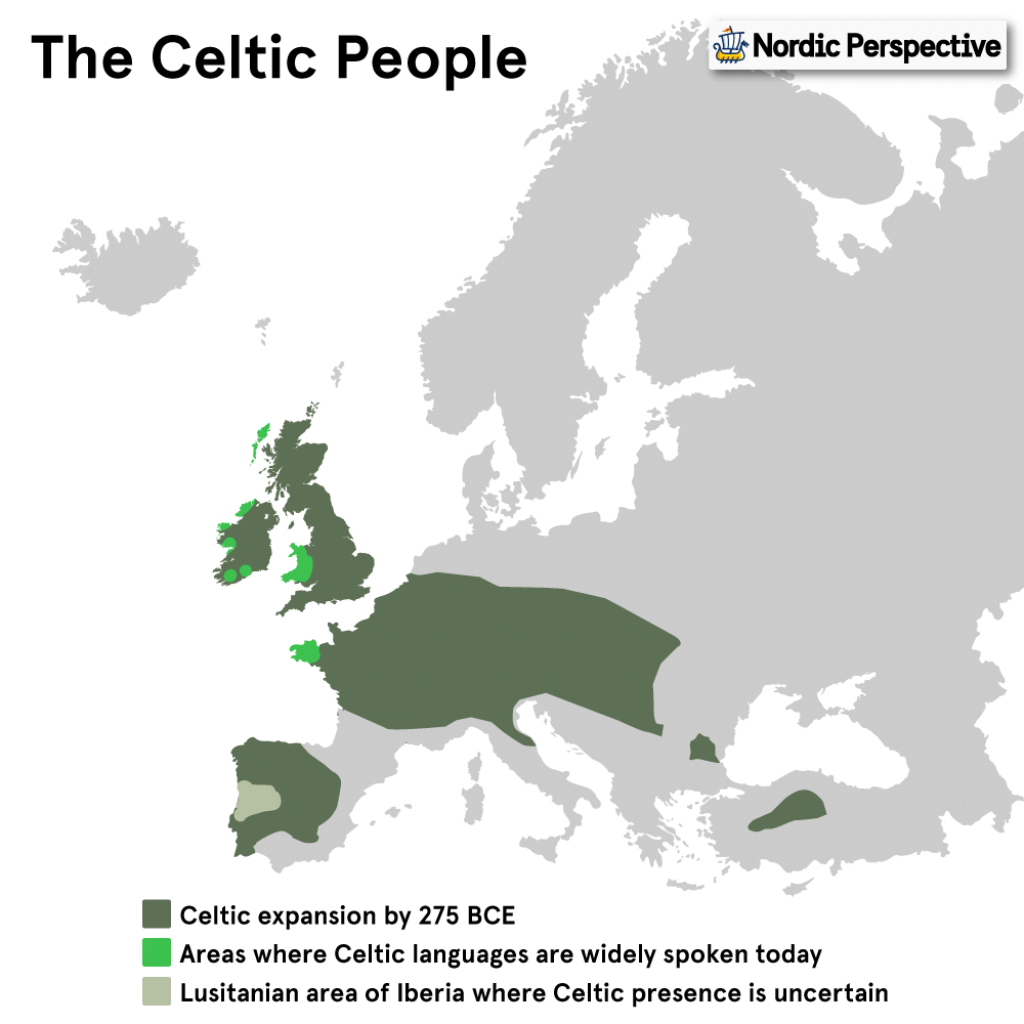
Which European Countries are Nordic, Germanic, and/or Celtic?
Let’s take a look at the languages spoken in each country right now and figure out if they can be classified as Nordic, Germanic, and/or Celtic.
Germanic, Nordic, and Celtic Languages Today
| Country | Nordic? | Germanic? | Celtic? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Albania | |||
| Andorra | |||
| Armenia | |||
| Austria | ✔️ | ||
| Azerbaijan | |||
| Belarus | |||
| Belgium | ✔️ | ||
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | |||
| Bulgaria | |||
| Croatia | |||
| Cyprus | |||
| Czech Republic | |||
| Denmark | ✔️ | ✔️ | |
| Estonia | |||
| Finland | ✔️ | ||
| France | Partly | Partly | |
| Georgia (country) | |||
| Germany | ✔️ | ||
| Greece | |||
| Hungary | |||
| Iceland | ✔️ | ||
| Ireland | ✔️ | Partly | |
| Italy | |||
| Kazakhstan | |||
| Latvia | |||
| Liechtenstein | |||
| Lithuania | |||
| Luxembourg | ✔️ | ||
| Malta | Partly | ||
| Moldova | |||
| Monaco | |||
| Montenegro | |||
| Netherlands | ✔️ | ||
| North Macedonia | |||
| Norway | ✔️ | ✔️ | |
| Poland | Partly | ||
| Portugal | |||
| Romania | |||
| Russia | |||
| San Marino | |||
| Serbia | |||
| Slovakia | |||
| Slovenia | |||
| Spain | |||
| Sweden | ✔️ | ✔️ | |
| Switzerland | ✔️ | ||
| Turkey | |||
| Ukraine | |||
| United Kingdom | ✔️ | Partly | |
| Vatican City |
How about DNA-wise then? Let’s go beyond linguistics and look at where Germanic, Nordic, and Celtic DNA “exists” today in Europe.
I use quotation marks because there is not one “gene” or similar that tells you if you are Germanic or Celtic, but I’m referring to the distribution of Y-chromosomal Haplogroups that are likely related to either Germanic, Nordic or Celtic roots
Germanic and Nordic DNA Markers Today
Germanic and Nordic ancestry go back together to the Nordic Bronze Age Culture, and even further to the Corded Ware and Funnelbeaker cultures during the copper age, both dominant and covering a similar area in Northern Germany and Southern Scandinavia.
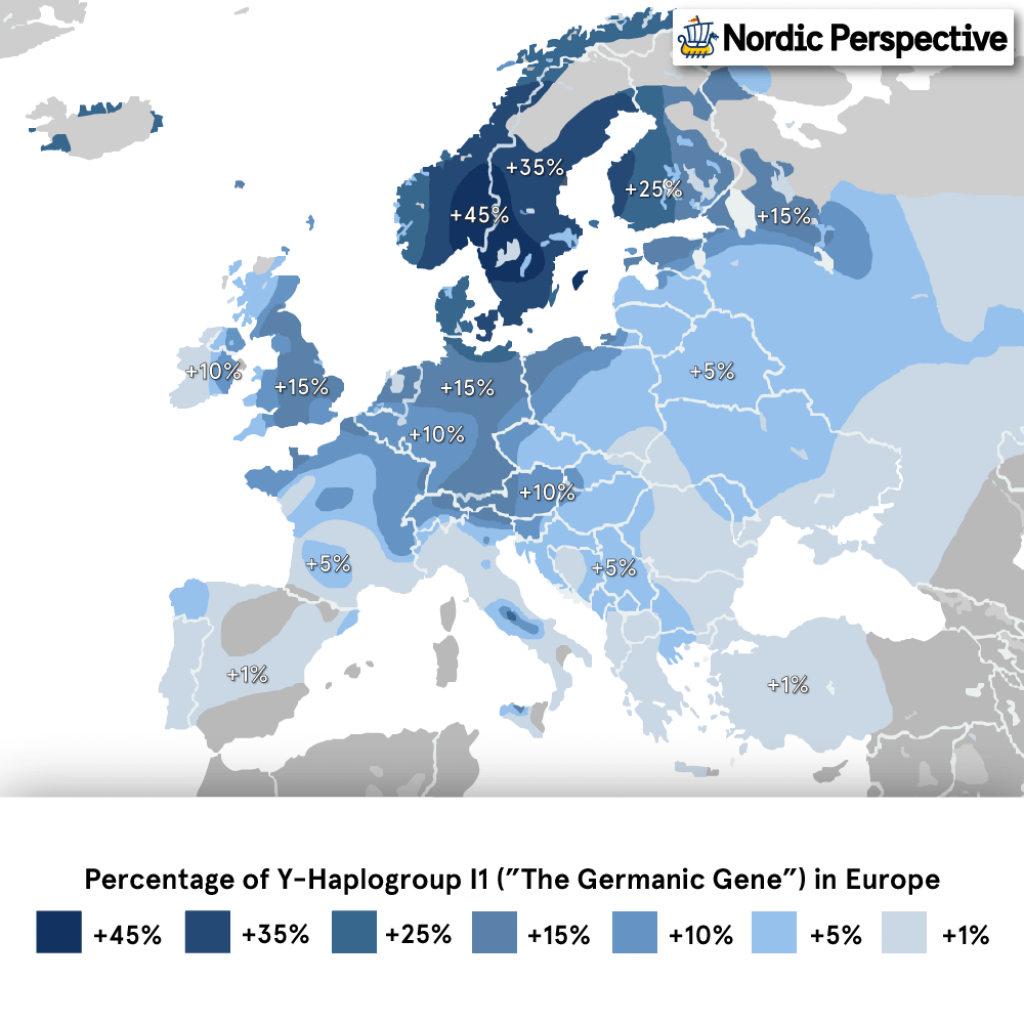
When comparing modern and ancient DNA-findings from the European region, scientists found a strong correlation to a specific haplogroup in regions where Germanic tribes migrated to and settled in.
They found that Scandinavians have the highest occurrence of this gene group — visible in at least 35% of the population, compared to around 15% in England and Germany.
Celtic DNA Markers Today
When looking at Celtic DNA markers, geneticists usually talk about three different haplogroups:
- R-L21 — often linked to the Insular Celts, and dominant among men in Ireland, Scotland, Wales and Brittany, as well as present in high frequencies in England and western France and also to a lesser extent in Iberia, Scandinavia and the Low Countries.
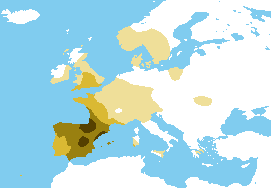
- R-DF27 — While L21 may have traveled through Belgium and northern France towards the British Isles, DF27 appears to have dispersed widely across France, predominantly moving towards the southern regions and Iberia.
- R-S28 (U152) — Stemming from an Alpine Bronze Age culture that set the stage for classical Celtic culture. It encompassed three interconnected cultures: Urnfield, evolving into Hallstatt (from 1200 BCE), and then La Tène (from 450 BCE), eventually expanding west to the Atlantic, north to Scandinavia, east to the Danubian valley, and further to Greece, Anatolia, Ukraine, and Russia.
Frequency distribution map of R-DF27 in Europe
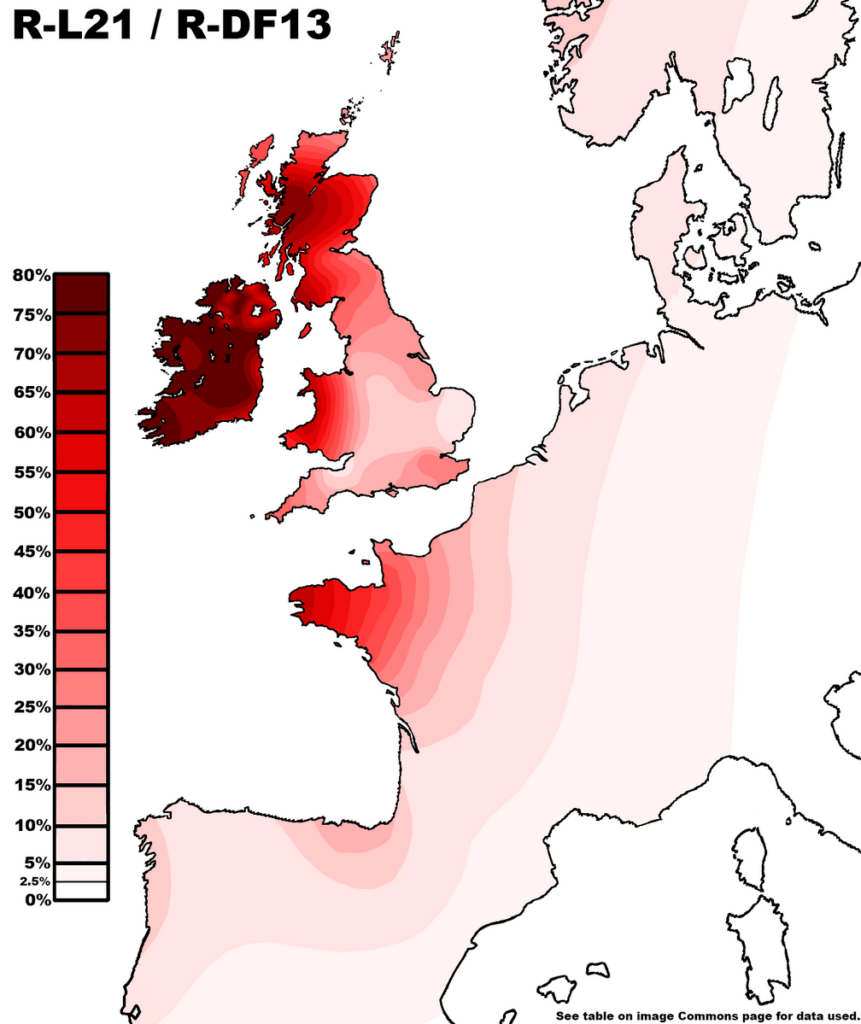
Expand this section for the full R-L21 Regional Persistence Dataset
Source: FamilyTreeDNA Country Data
| Region | % | |
|---|---|---|
| Republic of Ireland | 70.0 | |
| Ireland (Island) | 63.2 | |
| Scotland | 48.9 | |
| Northern Ireland | 48.2 | |
| Wales | 43.5 | |
| United Kingdom | 23.9 | |
| England | 16.5 | |
| France | 12.0 | |
| Portugal | 7.0 | |
| Norway | 6.1 | |
| Belgium | 6.1 | |
| Spain | 5.9 | |
| Netherlands | 4.5 | |
| Denmark | 4.2 | |
| Sweden | 3.2 | |
| Germany | 2.9 | |
| Italy | 1.5 | |
| FamilyTreeDNA Geographical Project Data | ||
| County Kerry Y-DNA Project | 82.0 | |
| Kilkenny Surnames Geographic Project | 80.0 | |
| County Roscommon, Ireland | 76.6 | |
| Clare Roots | 75.0 | |
| Greater Galway | 71.5 | |
| Cork Ireland | 68.0 | |
| Clans of Galloway | 56.5 | |
| Bretagne/Brittany | 55.0 | |
| Scots-Irish | 53.0 | |
| Aberdeen & North East Scotland | 50.3 | |
| Kintyre Roots | 50.0 | |
| Manx Y-DNA Study | 46.2 | |
| Isle of Lewis | 37.0 | |
| Northumberland | 35.3 | |
| Caithness & Sutherland (Counties) | 35.0 | |
| CORNWALL ADVANCED YDNA | 30.6 | |
| Orkney | 27.0 | |
| Normandy Y-DNA | 24.0 | |
| Shetland Islands | 22.2 | |
| Wessex, England | 20.2 | |
| Basque-DNA (Only counted those inside Basque region on project map) | 19.4 | |
| Devon | 19.0 | |
| Yorkshire | 18.4 | |
| Lancashire | 14.7 | |
| East Anglia | 9.5 | |
| Palatine | 3.5 | |
| Ireland yDNA Project Data (map used) | ||
| County Cavan | 80.9 | |
| County Tipperary | 80.0 | |
| County Mayo | 76.5 | |
| County Limerick | 64.3 | |
| County Dublin | 50.0 | |
| Combined DNA Project and Ireland yDNA Project Data | ||
| County Wexford Ireland | 53.0 | |
| British Isles by County Project Data | ||
| Middlesex | 33.6 | |
| Kent | 30.0 | |
| Herefordshire, Shropshire | 29.0 | |
| Lincolnshire, Leicestershire, Nottinghamshire | 22.3 | |
| Sussex | 20.9 | |
| Lancashire | 20.6 | |
| East Lothian, Mid Lothian, West Lothian, Lanarkshire | 19.8 | |
| Dorsetshire, Wiltshire, Hampshire, Berkshire | 19.1 | |
| Gloucestershire, Warwickshire, Worcestshire, Staffordshire | 17.7 | |
| Cheshire | 16.5 | |
| Derbyshire | 16.4 | |
| Northamptonshire, Buckinghamshire, Bedford, Hertfordshire, Huntingdonshire, Cambridgeshire | 14.4 | |
| Somersetshire | 9.0 | |
| Scottish Y-DNA Project Data | ||
| Skye | 66.0 | |
| Uist | 34.5 | |
Frequency distribution map of R-DF27 in Europe
Frequency distribution map of R-S28 (U152) in Europe
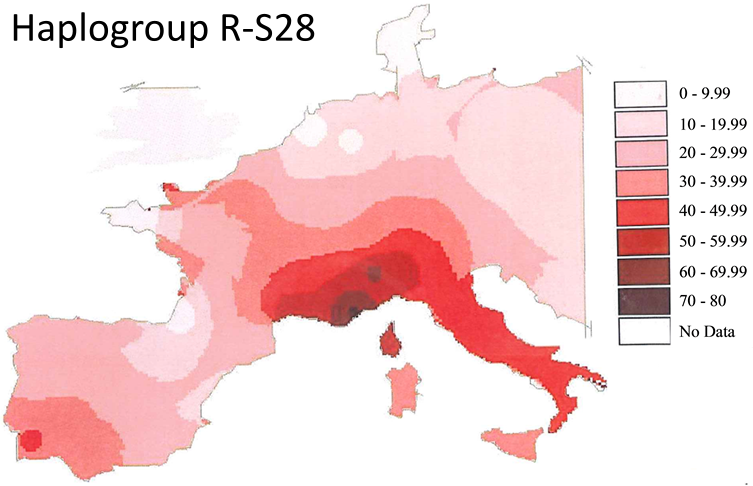
The purpose of presenting the prevalence of certain DNA markers linked to each culture group is to give a hint of where the Germanic, Nordic, and Celtic cultures took root in and around Europe.
Quick Answers
Is Scandinavia Celtic and Are Scandinavians Celts?
Scandinavia did not encounter Celtic influence as the Celts spread across large parts of central and western Europe during the Iron Age, meaning the region and its people is not Celtic in any meaningful way. Scandinavia was rather dominated by Germanic cultures stemming from the Nordic Bronze Age Culture at the time.
That said, there is plenty of Celtic heritage along the coasts of Scandinavia, as Vikings were prone to come home with both band members and slaves from the British Isles during the Viking age.
What Is a Celtic Viking?
Celtic Vikings, or Norse–Gaels as they can also be called, usually refer to the Vikings who settled in Ireland and Scotland during the Viking age. The Norse–Gaels dominated the majority of the Irish Sea and Scottish Sea region from the 800s up until the 1100s when Norse influence on the British Isles started waning.
Several Scottish clans have Norse–Gaelic roots, such as Clan MacDonald, Clan MacDougall, Clan MacLeod, Clan Oliphant. Several Irish families do as well, such as O’Donovan, Uí Ímair (later Crovan), Mac Oitir (later Cotter), MacAuliffe, MacManus, Doyle, and Reynolds.
By the way, if you're looking for some historically accurate viking apparel and wall art, I've designed a large collection of Norse wall art and apparel based on and inspired by actual archeological finds from Viking Age Scandinavia.
Sources:
https://royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/10.1098/rstb.2013.0384
https://www.jstor.org/stable/40849016
https://fof.se/tidning/2013/4/artikel/den-brutala-bronsaldern
 Scandinavian, Viking & Germanic Links Explained (With Maps)
Scandinavian, Viking & Germanic Links Explained (With Maps) The Germanic Tribes: History, Migrations, Timeline & Legacy
The Germanic Tribes: History, Migrations, Timeline & Legacy Why It Is Called Scandinavia (Origins & Meaning)
Why It Is Called Scandinavia (Origins & Meaning) Viking Origins, Ancestry & Why They Set Out on Adventure
Viking Origins, Ancestry & Why They Set Out on Adventure







My last name is Swihart. A shortened and anglocised version of the original name Schweinhardt. I am 10th generation American. The first Schweinhardts came to America in Pennsylvania in 1730 on a ship named the Pennsylvania. Im curious about the name Schweinhardt, and have done a lot of research and we all come from a common ancestor named Conrad Schweinhardt born in 1630 in Jungholzhausen, Germany where he was married and lived. Schweinhardt means Strong as a Boar.
In reality people of east Austria are a mixture of Germanic, and Slavic.
In the tenth century Bavarian tribes invaded the area that now corresponds to eastern Austria. They intermixed with existing Slavic people (Czechs, and Slovenes). This is why Y-haplogroup R1a-Z280 is higher than R1b-U106 in this part of Austria.
On an autosomal DNA level east Austrians are the most east shifted of all Germanic speaking people. They cluster close to Hungarians, and Czechs.
West Austrians cluster with Bavarians, and Swiss Germans. While east Austrians speak a Bavarian dialect they cluster closer to East Germans than they do to Bavarians.
Thank you for time consuming research, together with a personalized touch.Like you Im somrthing of a “Nerd’. Ive been an ancient history buff since my re-teen years. I play music professionally, mostly Blues and jazz[ http://www.jukejointjokers.com, sorry no YouTube yet but its coming|
I also write articles for chess.com and historical fiction, and supernatural as well.
Thanks for reading Kevin!
I think it’s important to understand our history in order to understand ourselves sometimes, without getting lost in the rabbit hole of course. 🙂
Cool musical projects, keep it up!
Your discussion is focussed on the current existing languages. The picture that has emerged from DNA studies is vastly different than that of the languages survival picture, so are the cultures. Many western europeans share significant DNA related to the Celts, especially when looking at their Y-DNA. In my case, it turns out that I descend from the Celts of “la Tène Culture”, who where located in 600 B.C. in Champagne Ardennes, East of France (near Verdun), Southern Bavaria. There are many documented archeological sites and resources available. You will find many interesting references to the Celtic culture, included in them. For example, the names of towns or villages in France and Belgium which terminate with a “y”, are names of celtic origin!… The Celtic language in these regions was replaced by latin, just like the language spoken by the Franks (Netherlands, Belgium, Northern France) was replaced by latin. Many aspects of the modern cultures have survived beyond the language: The Franks for example adopted many traditions from the Celts as well as the Romans. Celtic desscendance should not be limited to Ireland/Scotland and should include Belgium, France, Italy, Switzerland and Austria at a very minimum.
Thanks for providing some very interesting Celtic perspectives! I agree that Belgium, France, Italy, Switzerland and Austria have strong Celtic ties, as evident in the extent of Celtic influence around 275 BCE (which is specifically the La Tene Culture in action!).
When discussing DNA, Europe certainly is a melting pot of all kinds of origins and roots with intriguing histories attached to each one! I should definitely try to clarify when I’m referring to linguistic or genetic links to not cause confusion or step on any one’s toes.
I will go through and clarify some parts of the article as well as try to bring in the DNA discussion throughout. Again, many thanks Michel!
Karl,
Thank you for for your response. I think that is what need to be done. I am also curious about the Celtic Scandinavians. I do have a small scandinavian component in my autosomal DNA. I tend to believe that it originates in early 1800 and is mostly likely related to the Napoleonic wars occurring in Northern France and Belgium. Napolaéon’s army has a significant number of soldiers from many European countries, including scandinavians. I wonder if the Napoléonic wars had an impact on Celtic Scandinavians. Regarding the Vikings, France saw many invasions along the coast and rivers (such as the Seine) of the northern half of France (700-1000). There is little doubt that the Vikings had a significant influence in Normandie (see for example the lineage of William the Conqueror and his vassals}.
Finally, I agree with you on the very complex situation of DNA distribution in Western Europe, including the British Isles. There is just too much history to believe that the DNA distributions are specific to modern countries
This is top-notch! I wonder how much effort and time you have spent to come up with these informative posts. Should you be interested in generating more ideas about Website Design, take a look at my website Webemail24
This was a delight to read. You show an impressive grasp on this subject! I specialize about SEO and you can see my posts here at my blog Article Sphere Keep up the incredible work!
Your map, The Germanic People, is very helpful in understanding the people from north west Europe. I posted this map in my article, nordic-homeland.blogspot.com .